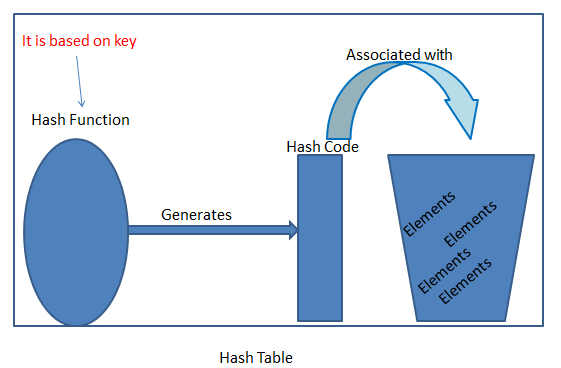
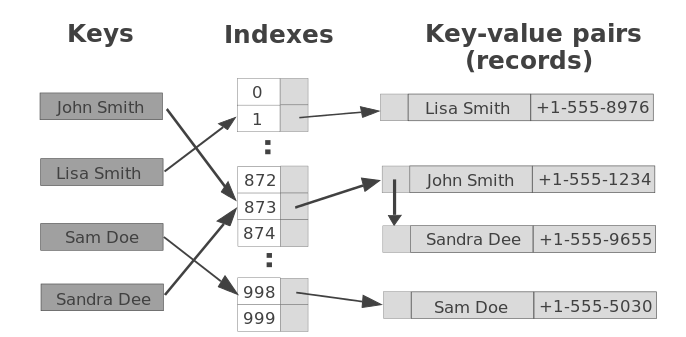
A hash table (also called a hash, hash map, unordered map or dictionary) is a data structure that pairs keys to values. Its a technique to convert a range of key values into a range of indexes of an array. Its used to implement an associative array, a structure that can map keys to values. A Hash Table uses a hash function to compute an index into an array of buckets or slots, from which the desired value can be found. From Wikipedia.
Hash table operations are performed in two steps:
- A key is converted into an integer index by using a hash function.
- This index decides the where the key-value pair record belongs.
Its very useful to find out, e.g. a) number of occurences of each word in a book, b) similar problems, like finding number of unique words. c) given a log containing UserId, ProcessId, starTime, endTime and resource consumption, finding user with highest resource consumption. d) In a compiler, a hash table will likely be used for keyword and identifier storage because a compiler needs quick access to this information, e) another most well known use for hashing is in cryptography.
Although hash tables provide fast insertion, deletion, and retrieval, they perform poorly for operations that involve searching, such as finding the minimum and maximum values in a data set. For these operations, other data structures such as the binary search tree are more appropriate.
Complexity Source
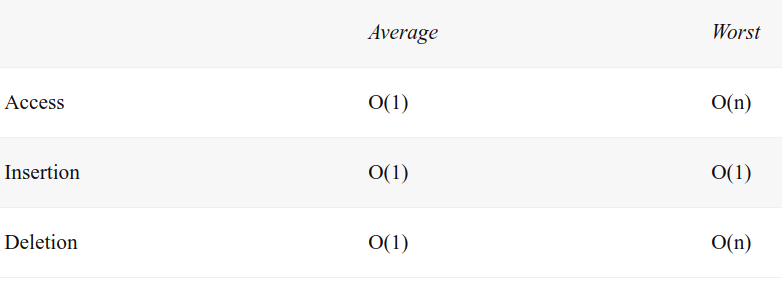
Hash Function
The Hash-function takes a key and converts it to a number which will be the index at which to store it. In my hash() function below, I am computing a hash value by summing the ASCII value of each character of the string (the argument passed-in) using the JavaScript function charCodeAt() to return a character?s ASCII value after multiplying the ASCII value by a multiplier H, which in this case, is an odd prime 37. And the reason to choose 37 being, by some empirical research, if we take over 50,000 English words (formed as the union of the word lists provided in two variants of Unix), using the constants 31, 33, 37, 39, and 41 will produce less than 7 collisions in each case, while creating a hasing function.
Note that some form of remainder method (modulo arithmetic) will typically be present in all hash functions, since the result must be in the range of slot names. In the below cae (total %= this.table.length). Because, the hash function will turn its passed-in argument and return an integer in the range of slot names, between 0 and m-1. A perfect hash with no collison, e.g. can be created if the number and construction of the keys are known factors. For example, a perfect hash for a list of ten product numbers that are sure to differ in their 4th and 5th digits can be easily constructed like so, unsigned hash(unsigned pid).
{ return pid / 1000 % 100; }
However, in the above, notice that even though there are only ten product numbers, a table of 100 buckets must be created because the resulting hash values are at least two digits. This is a huge waste of space, but if the range is forced into an array of 10 buckets, the right digit of the hash values may match hence the chances of a collision.
So, effectively, the hash function changes the passed in argument to a number. so that they can be used as array index. So, if I want to save my name ?Paul?, just convert this name to integer first with some kind of of hashing formulae. In a super simplied form it will work as below?
// To insert “John”var k = hashFunc(“Paul”); arr[k] = “John” // this takes O(1) time // Now lookup for John:- var k = hashFunc(“John”) ; var name = arr[k] ; console.log(name); //prints John
Hash table is like a bucket, represented as an empty array initially. When initializing the hash table we create an array containing a fixed number of these buckets.
var allBuckets = [, , , ] And in order to insert a value inside our buckets, i.e. insert a key ?x? with the value 10 1. Use has function to get bucket index 2. Push key-value pair into bucket
Collision-Resolution
Even with an efficient hash function, it is possible for two keys to hash (the result of the hash function) to the same value. This is called a collision, and we need a strategy for handling collisions when they occur. In my implementation below, this is taken care of by the put() function. The put() function receives the array index value from the hash() function and stores the data element in that position. But only after checking that after the kkey value is hased (with the hash() function) there?s no collison. And this can be done in two ways – separate chaining and linear probing (both have been implemented in the below code).
A generic HashTable Implementation in JavaScript
Some very simple application of associative-arrays (non-hashed) in solving common problems
Problem – Check Permutation: Given two strings, write a method to decide if one is a permutation of the other.Key points to solve this problemA> It is assumed that the characters are stored using 8 bit and there can be 256 possible characters.B> We will create a Hashmap with the charCodeAt number of the characters of the first string as keys and the number of occurances of the character as value; So, at the first occurance of the character increment, the value of the key by 1 and at the second occurance increment the value by another 1. Result, for each character, the no of occurance will be equal to that key’s value’ All the rest of the values of the Hashmap will be filled with zeros.Then go through the second string and for each character, look up the hash table for that key-value pair. And decrement the value by one, when that key is found the first time, and by another one, if the character occurs twice. If the two strings are permutations then they should have the same unique characters each with the same number of occurrences.So, none of the second for loop’s if condition can have a negative value for a key, if the 2 strings are permutation of each other.C> Create a hash-table of size 256 (i.e. 256 elements) and initialize all values with 0’s.D> With the for loop, for each character in str1, I am setting its “UTF-16 code unit” value (with charCodeAt method) as the key (incex position) for that hash_table.E> Compare the occurrence of each character, using the char value as index into an array of counts.Time Complexity of this solution : O(n) and Space Complexity: O(1)
Another application of implementing associative-arrays (non-hashed) for solving daily problems
Implement a function to remove duplicates from an array and returning an array of only unique elements
Further example of associative-arrays (non-hashed) ? This is from a Google Interview Question for Software Engineers
Problem Statement ?
you are on a biz trip and travelling from one city to another. you have a stack of unsorted flight boarding passes. only departure city and destination city are on the boarding pass. how do you find the first departure city and your final destination city, write the solution in javascript.
Key solution strategy ? First note, that each city will be shown up in the boarding ticket 2 times (one for departure and one for arrival) ? Except the first city (being the first departure) and the last city (being the last arrival) which will show up only once. So arithmatically all cities will cancel each other, except the first departure and final arrival city.
A) Store the cities in a hashmap.
B) We?re going to map each city to the net in and out number ( -1 or +1 ). Then traverse through the hashmap.For departure, decrease value of net in and out, for arrival, increase value of net in and out.
C) If a departure-city has not been stored yet in the hashmap, meaning this city has not been travelled yet, So store it with a value of -1
Else, being a departure-city decrement its value by 1
D) If an arrival-city has not been stored yet in the hashmap, meaning this city has not been travelled yet, So store it with a value of 1
Else, being an arrival city, increment its value by 1.
E) So, when the Hashmap is fully constructed, the value of cities will cancel each other, except the First arrival and final destination.
So, scan through the final hash table to find +1, which is the destination, and -1, which is the departure.
Measuring performance
For the generic HashTable program that I wrote at the top of this page, lets design a test that generates 100,000 keys and values, then measures how long it takes to insert (put()) and then read (get()) them from the hash table. I took the makeid function from StackOverflow that would generate 100,000 character string composed of characters picked randomly from the set [a-zA-Z0-9]. I use console.time and console.timeEnd to measure how fast our hash table is.
And it looks like the Linear Probing technique runs much faster.
The great confusion about Hash vs Objects in JavaScript
Fundamentally, every object in JavaScript IS a hash. This is a hash of object?s properties and methods. Every time I call object?s method, property, or just reference any variable, I perform an internal hash lookup.
Why I need a hashtable instead of just a non-hashed associative array, which definitely will be simpler to implement
When using a hashtable, I compute the hash code of a given key to find the associated value. The hashcode is an index in the underlying array of the hashtable. This means that finding a key in a hashtable is as fast as accessing an array by index. So, while searching, the hash table mechanism gives me O(1) performance for any given key search, since a constant amount of time is required to compute the hash value and then index the hash table at that location. Accessing an array with an index (e.g. myArray[0] ) is instant; it doesn?t require any searching, because the runtime of the languages knows exactly where to find this value.
And if I do not use a HashTable, I still need some sort of search mechanism. And if I choose, Binary Search Tree, it?s O(log n) not O(1). And if I don?t have a search mechanism at all (i.e. I am searching the entire array from top to bottom to find my key), my performance is O(n).