UX steps by steps
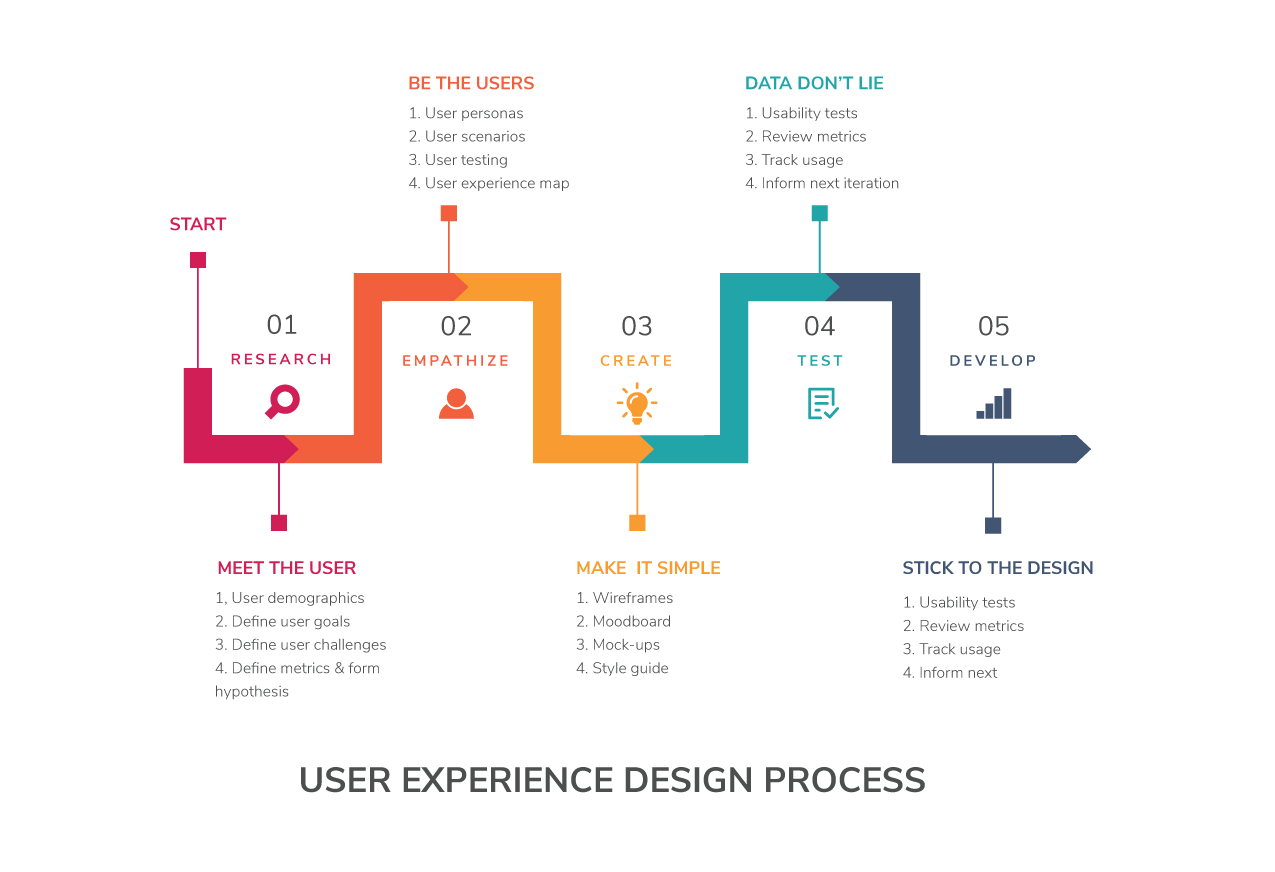
RESEARCH | Meet the users
RESEARCH
Figure out what are needed to research:
- Similar cases
- Successful approaches and solutions
- People opinions and reactions
Google about everything that we are curious about the users and the case. The final goal is putting ourselves in user?s shoes and understanding their problems and what they need.
INTERVIEW + OBSERVATION
Talk to real users or potential users, clarify your assumption and understand them more.
SURVEY
The survey may be useful if we need more quantitative research and large amount of users, or have to the interview remotely.
EMPATHISE | Be the users
EMPATHY MAP
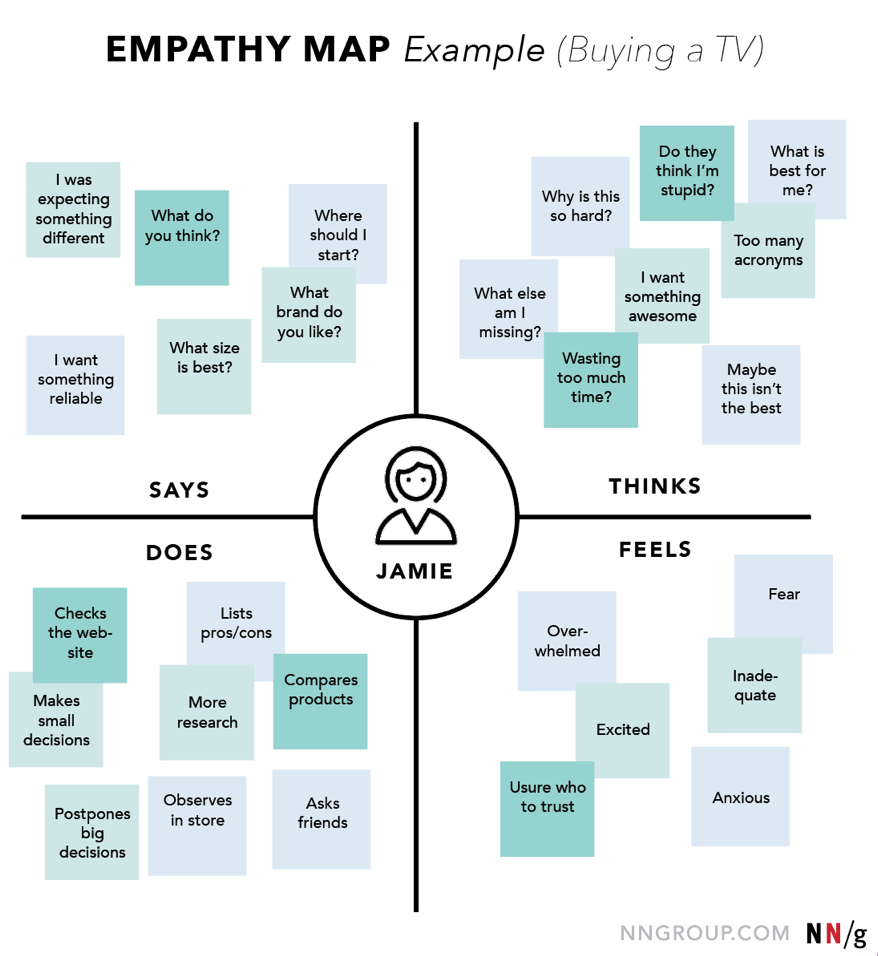 https://www.nngroup.com/articles/empathy-mapping/
https://www.nngroup.com/articles/empathy-mapping/
Benefit of empathy map:
- Remove bias from our designs and align the team on a single, shared understanding of the user
- Discover weaknesses in our research
- Uncover user needs that the user themselves may not even be aware of
- Understand what drives users? behaviours
- Guide us towards meaningful innovation
PERSONAS
Write down a situation in which users use the product. From that, how to design the product that meets those needs.
Without identifying the various characteristics of the user groups visiting our site, we cannot hope to design an experience that includes the key elements that each type of user needs. Instead, we could end up creating a website that doesn?t perform well for anyone.
STORYBOARD
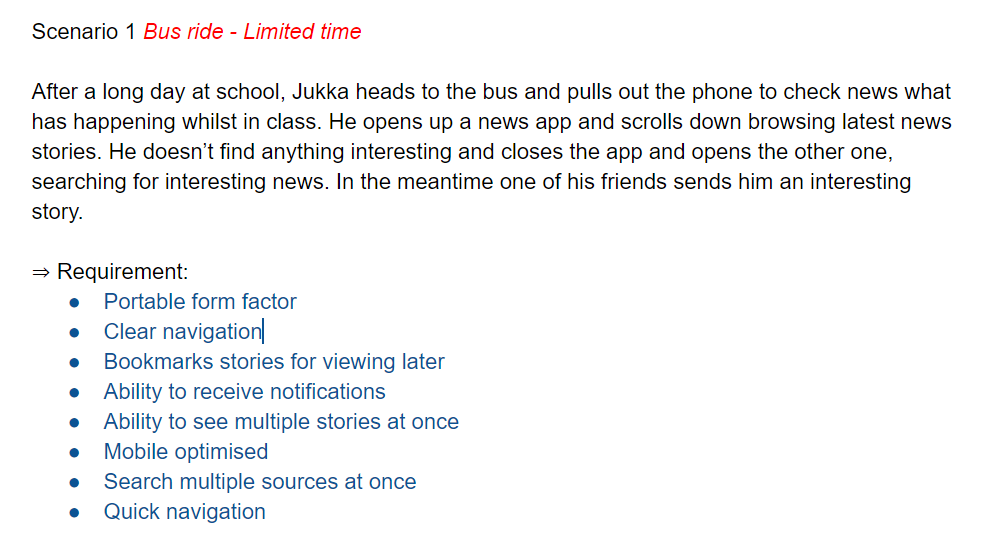
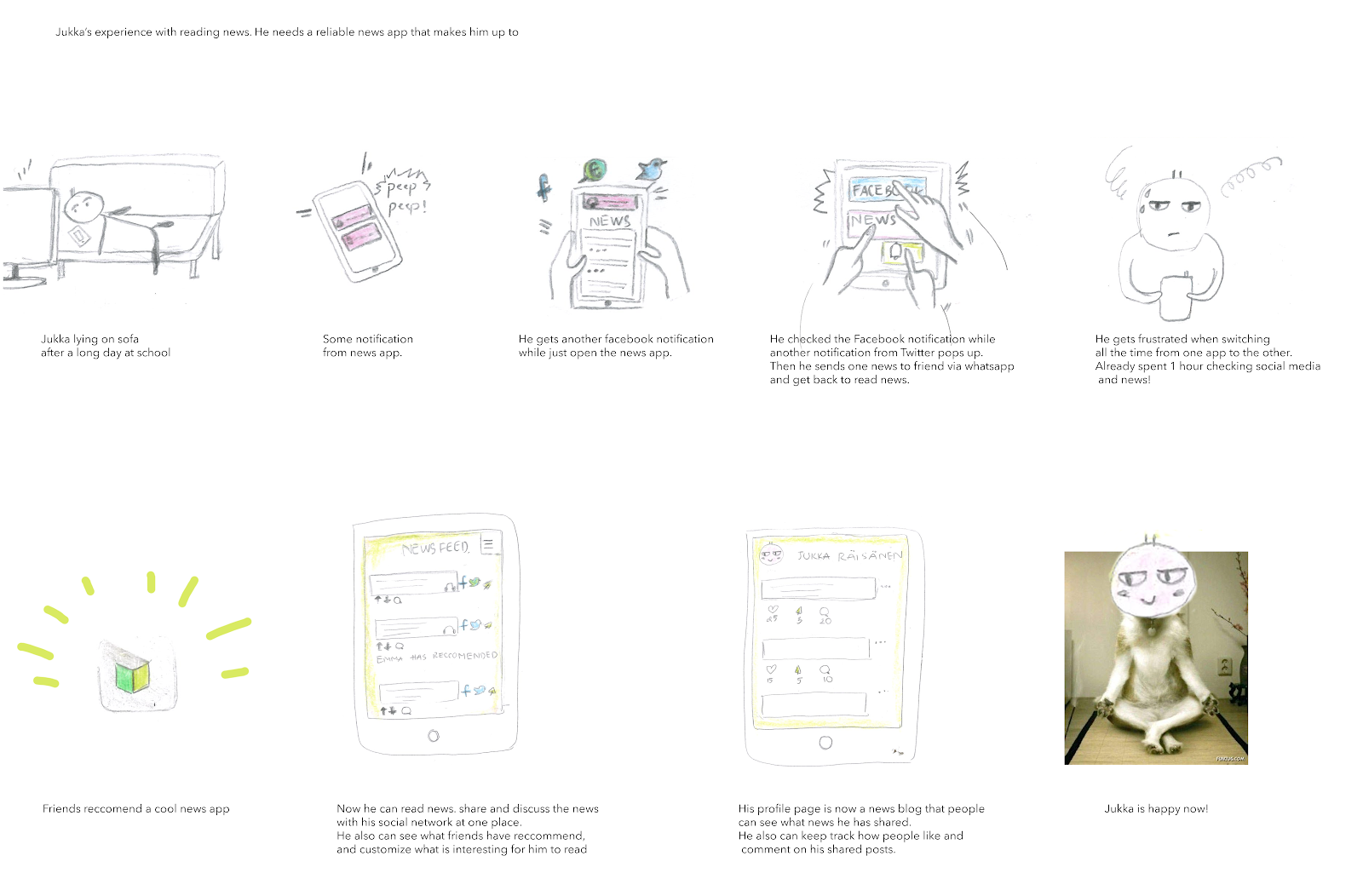 Scenario of one student who is often busy reading news and checking social media at the same time
Scenario of one student who is often busy reading news and checking social media at the same time
- User scenarios can be used in the ideation phase of a design project. This is where visualising how a user will use a product or service will help generate design ideas. A fundamental point to bear in mind is that user scenarios do not represent all possible users. Instead, they typically account for only the most common users or user motivations (The Interaction Design Foundation, 2018)
- Describe how and in which kind of situation the product or service would be used (put in context).
- Start a scenario with the triggering event and describe the sequence of actions and results with a right level of details.
- Scenario => requirements for the prototypes, what functions need to be built for the needs of users in the scenarios.
IDEATION | Concepting
IDEATION MAP
From the problem worth solving, list down the negative feelings when the problems are unsolved (left) , and the positive feelings when the problem solved (right). Based on the feelings, think about the solution for that.
 Lean Service Creation by Futurice. https://www.leanservicecreation.com/material/LSC%20Handbook%201.82.pdf
Lean Service Creation by Futurice. https://www.leanservicecreation.com/material/LSC%20Handbook%201.82.pdf
SPRINT INDIVIDUAL IDEATION in 6?10 minutes
Create and accept as many ideas as possible, no critique, say yes, don?t be too critical to yourself.
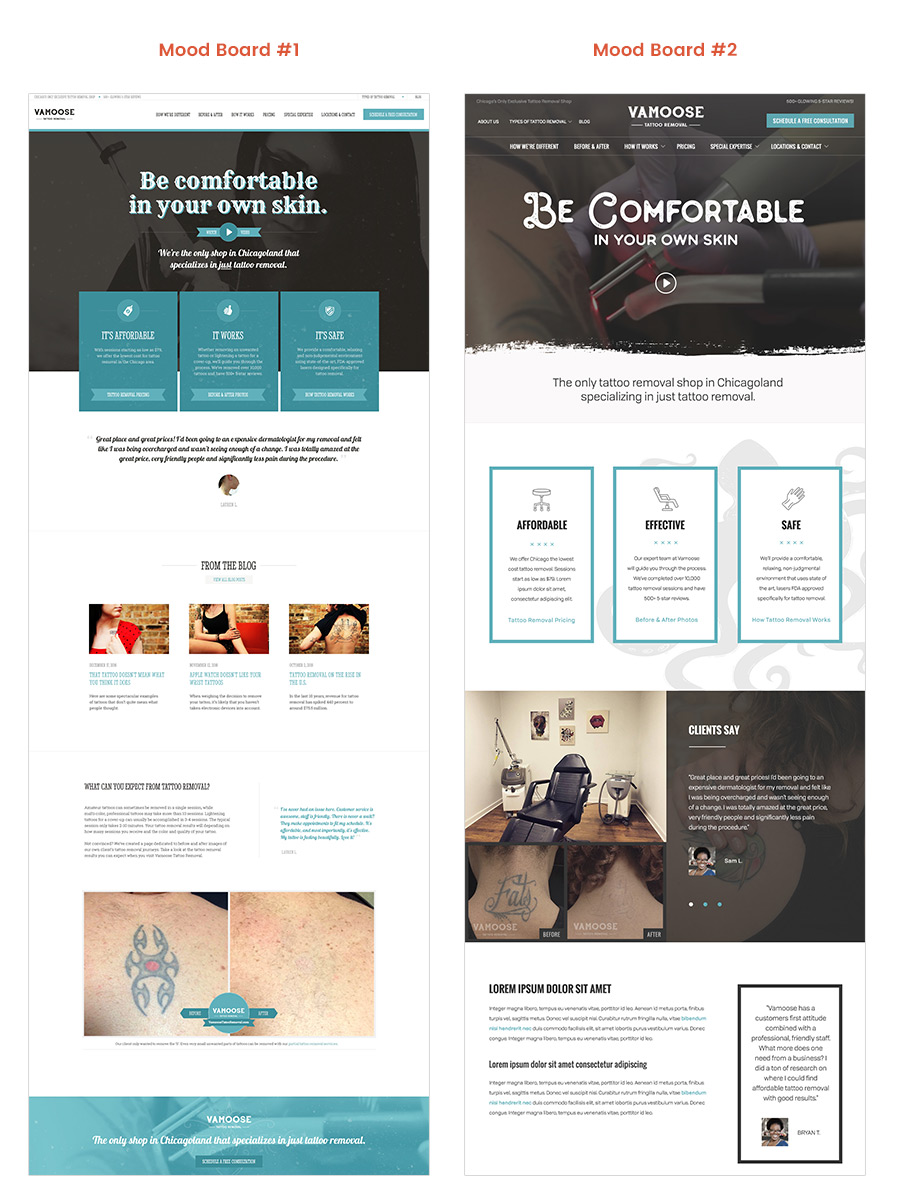
MOODBOARD
Think about the color scheme, style guide and the visual look of the design.

PROTOTYPING | Make it real
FLOWCHARTS
Flowcharts are diagrams that show the steps in a process
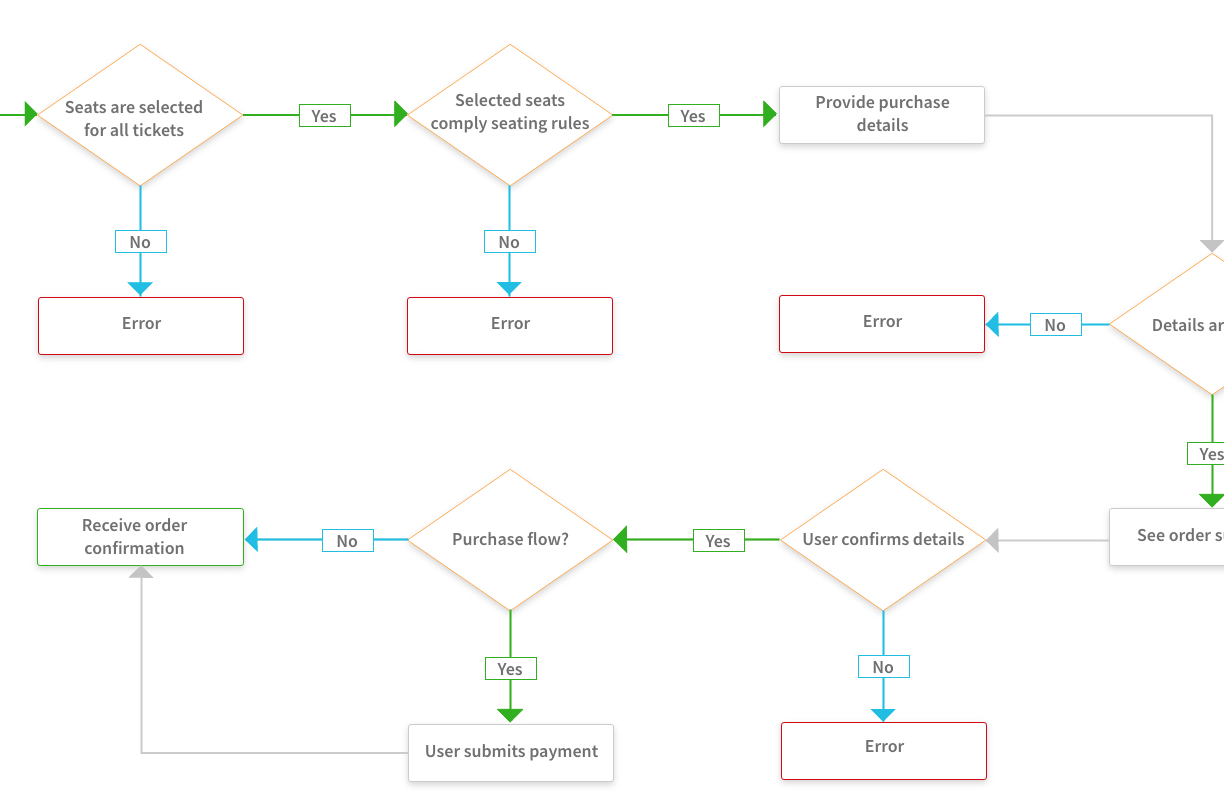 Flowchart for buying ticket and selecting seat
Flowchart for buying ticket and selecting seat
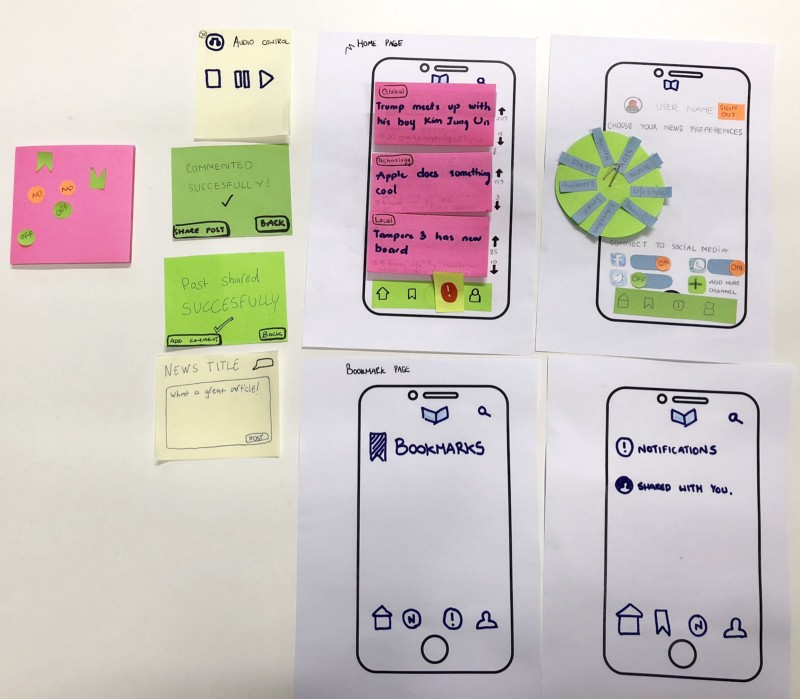
PAPER PROTOTYPE
Paper prototyping is sketching screenshots on paper as substitutes for digital representations. It is fast and perfect for early stage conceptualising. Even though in some case we do not need to do paper prototype, especially when we redesign something existing already. However, it is still an intuitive and flexible way so that every designer usually start with.

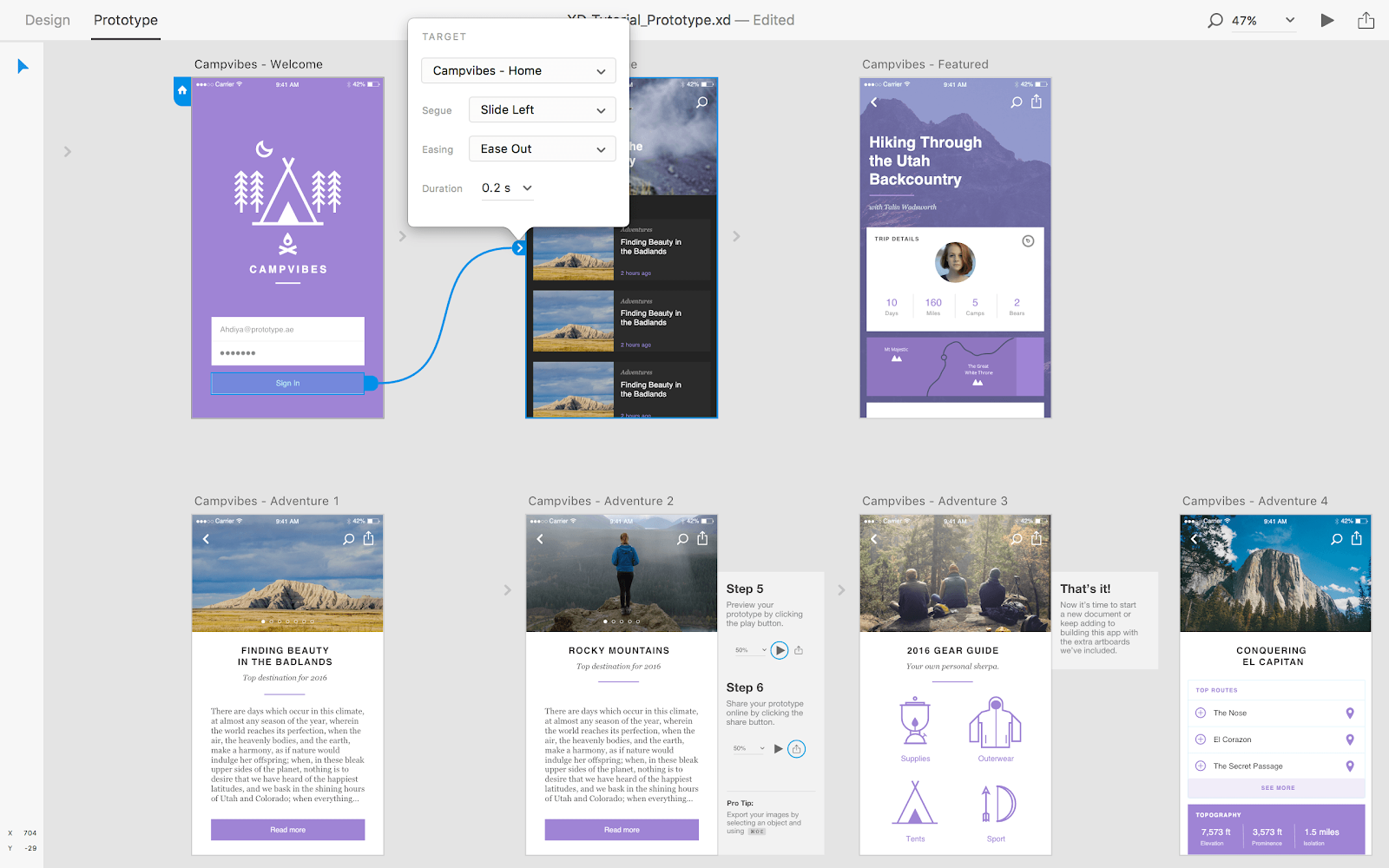
DIGITAL PROTOTYPE
WIREFRAME
Use tools as Sketch, Figma, Axure, Adobe XD, Balsamiq and so on for designing wireframes that make sense.

ACTUAL DESIGN
Using design software as Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD, or even Photoshop or Illustrator to design the actual interface.
TESTING | See how it works
- Prototype should be real enough to get an authentic response in order to validate or invalidate a hypothesis.
- Think critically about what to build in prototype in order to get the feedback.
- Test goal is to find out if the solution works as planned or provides
TESTING IN PAPER PROTOTYPE
Plan the script
Roles: who will take care of prototype, who makes notes, who facilitate and talk to the users during the test
What to test (steps- results)
Beginning of the test
Introduction to users ( brief user privacy ethics, explain the scenario what is product for or in what situation, imagine you are now?.)
Ask users think aloud so we can know what is they think right away at that moment
During the test
Take note how users act, do and how well they understand the task.
Give a clear instruction to user
TESTING IN DIGITAL PROTOTYPE
Invision and Figma Prototype is a good tool for mock up the prototype that allow users click and test the prototype without actual coding.
ITERATION | Get feedback and develop further
Develop the design based on real feedback from clients