
Just recently I made the startling discovery as to how easy it was for a computer hardware recycler to rife through the personal files of a donated machine by simply removing the hard drive and connecting it into a PC as an external USB device.
The Problem
How were they able to do this?
Quite simply, the hard drive was unencrypted and the files could be accessed without any form of authentication. Similarly, a state-sponsored hacker could employ the same tactic at airport security by confiscating your laptop for ?inspection?. With some uninterrupted time alone, there is a possibility that any one of the following could happen:
- A 1:1 clone of your hard drive is made for analysis and research into your computer habits and personal affairs.
- Insertion of malicious script files configured to run at system startup. The possibilities for further exploitation from here are endless (Keylogging, ransomware or other surveillance tools).
- Modification to any file on your hard drive thereby bringing the integrity and authenticity of your data into question. This is especially critical to research papers, news pieces, and other research.
Traditionally, big corporations and governments would have you think the actions they take to improve security are for the greater good and your safety.
The inspection of your data is necessary to identify and apprehend criminals and violent extremists.
Although there is merit in employing mass surveillance tactics, the tradeoff in terms of privacy and freedoms is considered by some to be too great as exhibited by this Motherboard VICE piece. The distrust in these state-owned corporations grows by the day and many individuals have taken a stand to protect their privacy, freedoms, and data.
Principle of Hard Drive Encryption
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) outlines three states of data to protect:
- Data at rest: Stored data which is not yet in use.
- Data in transit: Data currently moving between two locations.
- Data in process: The modification of data through computation or processing.
To resolve the issue mentioned above is to protect the data at rest. In this case, the simplest way to prevent unauthorised access to your computer data is to make said data unreadable unless you have the authorisation key.
Encryption at its most basic level is using an algorithm (a cipher) to jumble up data based on a key. The difference between the two broad categories of encryption lies in whether the key used to encrypt the data is the same key used to decrypt (symmetric) or not (asymmetric).
To encrypt one?s boot hard drive is to implement Full Disk Encryption (FDE). The following sections will outline an FDE option for Windows, macOS and Linux on a Pre-Boot Authentication (PBA) level i.e. requiring authentication to decrypt the disk at system startup.
Full disclosure: I am not, in any way, affiliated with any of these software vendors nor am I receiving any payment from these vendors to discuss their products.
Encryption on Windows
Being one of the most widely used operating systems on the planet for workstations, it comes as no surprise that Microsoft Windows has the widest range of software solutions for FDE. We?re only going to discuss the two arguably most popular encryption platforms for Windows.
VeraCrypt (Formerly TrueCrypt)
Before we discuss VeraCrypt, we?re going to do a quick dive into the interesting history behind its predecessor: TrueCrypt.
A Brief History
Existing as an open-source project maintained by anonymous developers, TrueCrypt was one of the most common FDE programs in circulation for Windows since 2004. The term ?was? is appropriate because TrueCrypt was shut down and re-released as VeraCrypt in 2014.
The unexpected shutdown was met with a great degree of scepticism by the security community. Many suspected there were government forces at play mandating the provision of backdoors in the software for unfettered access whenever required. These concerns were backed by the following message posted by the developers:
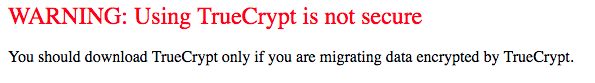 Image Source: http://truecrypt.sourceforge.net/
Image Source: http://truecrypt.sourceforge.net/
To further muddy the waters, an independent third-party audit was completed on the TrueCrypt code to identify security vulnerabilities. Matt Green of the Johns Hopkins University in conjunction with the NCC Crypto Services Group reported:
??Truecrypt appears to be a relatively well-designed piece of crypto software. The NCC audit found no evidence of deliberate backdoors, or any severe design flaws that will make the software insecure in most instances.?
TrueCrypt Reborn: VeraCrypt
The security vulnerabilities identified by Green and the NCC team were addressed in VeraCrypt which forked from the original TrueCrypt project. VeraCrypt offers a PBA option and supports a wide range of symmetric encryption algorithms. The latest release at the time of writing is v1.23 released on September 2018. VeraCrypt also enables you to create ?encrypted volumes? on your disk for a deeper level of data concealment. As we?re mainly discussing PBA options in this piece, we?ll ignore these other features for now.
Following a straightforward installation process, you?re met with a simplistic interface:
 VeraCrypt Application Start Display
VeraCrypt Application Start Display
To encrypt the entire drive for PBA, you?d go to System -> Encrypt System Partition/Drive. The user-friendly prompt walks you through whether you?d like to make your drive completely hidden and encrypted for that extra level of security (Most people will not need this option!) and also whether you?d only like one partition or the whole disk encrypted. The former is great for systems where your disk is partitioned into system/data type configurations.
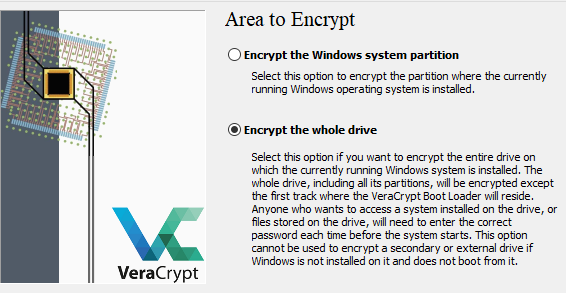 Partition vs. Full Drive Encryption
Partition vs. Full Drive Encryption
You?re also spoilt for choice in terms of encryption and hashing algorithms. The use of symmetric AES encryption and a SHA-256 hash is a good industry standard to proceed with for most consumer applications.
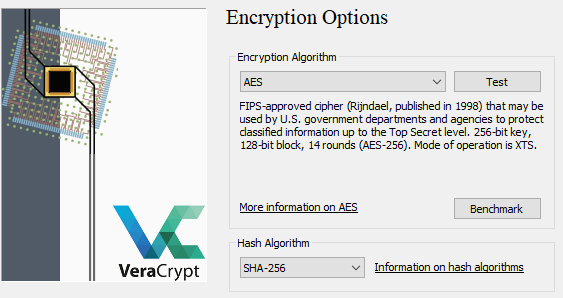 AES and SHA-256 Are Good Choices For Most Applications
AES and SHA-256 Are Good Choices For Most Applications
After setting your STRONG password and salt via random mouse movements it?s highly recommended to create the rescue disk provided by VeraCrypt as part of the setup process in case you have any issues with your encryption. This disk can decrypt your volume (Provided with the correct password of course) and also help you recover your installation.
Finally, VeraCrypt will ask how many times you?d like your data to be overwritten before encryption (To prevent data recovery specialists from recovering the data). For most users, no wiping will be necessary. You?ll be prompted for a reboot to test the encryption process.
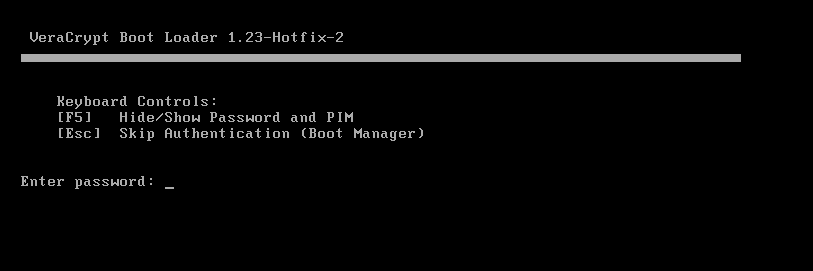 Pre-Encryption Test Boot
Pre-Encryption Test Boot
If this goes well, VeraCrypt will autorun after boot up and you?ll begin the encryption process.
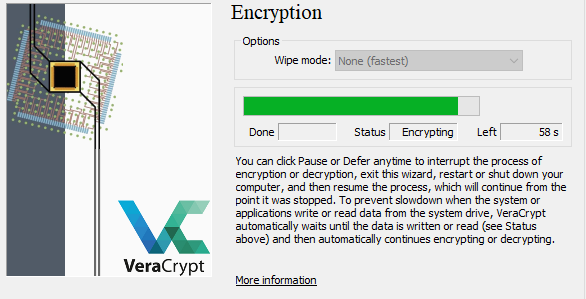 Final Encryption
Final Encryption
Voila! You?ve got PBA via VeraCrypt!
BitLocker
Introduced by Microsoft in 2015, BitLocker is the baked-in Windows encryption mechanism and a recommended alternative to the superseded TrueCrypt program. BitLocker employs AES-XTS symmetric encryption with key sizes up to 256-bit and is capable of being used in PBA mode. As such, its encryption mechanism is considered relatively strong.
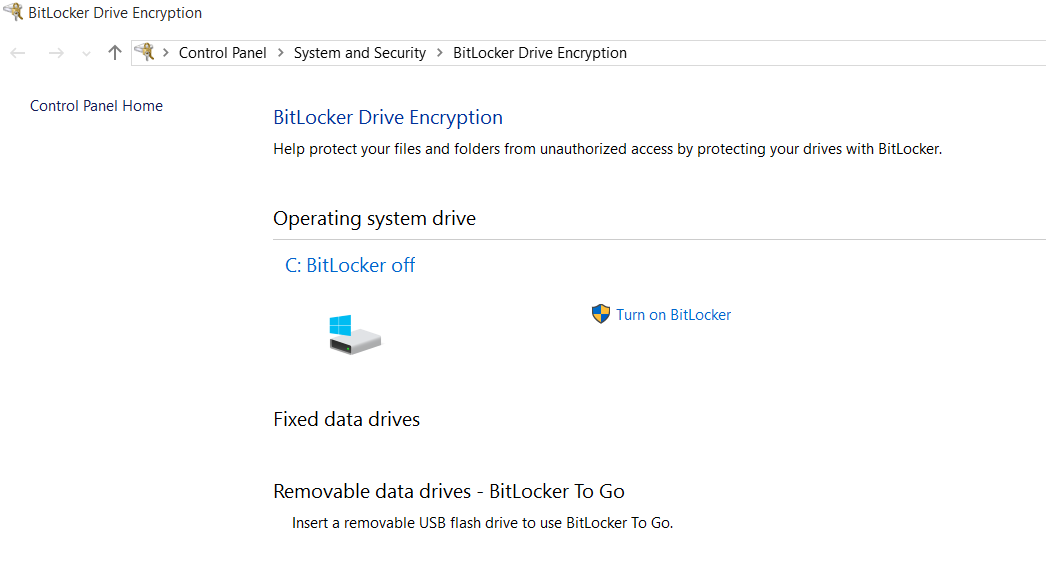 BitLocker for Windows 10
BitLocker for Windows 10
Now when you start configuring BitLocker, it may say that you don?t have a compatible Trusted Platform Module (TPM) which is essentially specialised hardware to generate encryption keys.
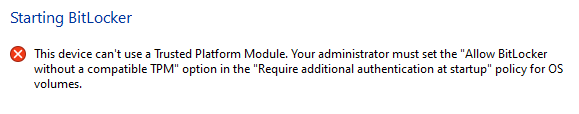 Error Message for No TPM
Error Message for No TPM
You can bypass this error by setting a local group policy through the Local Group Policy Editor (Run GPEDIT.MSC):
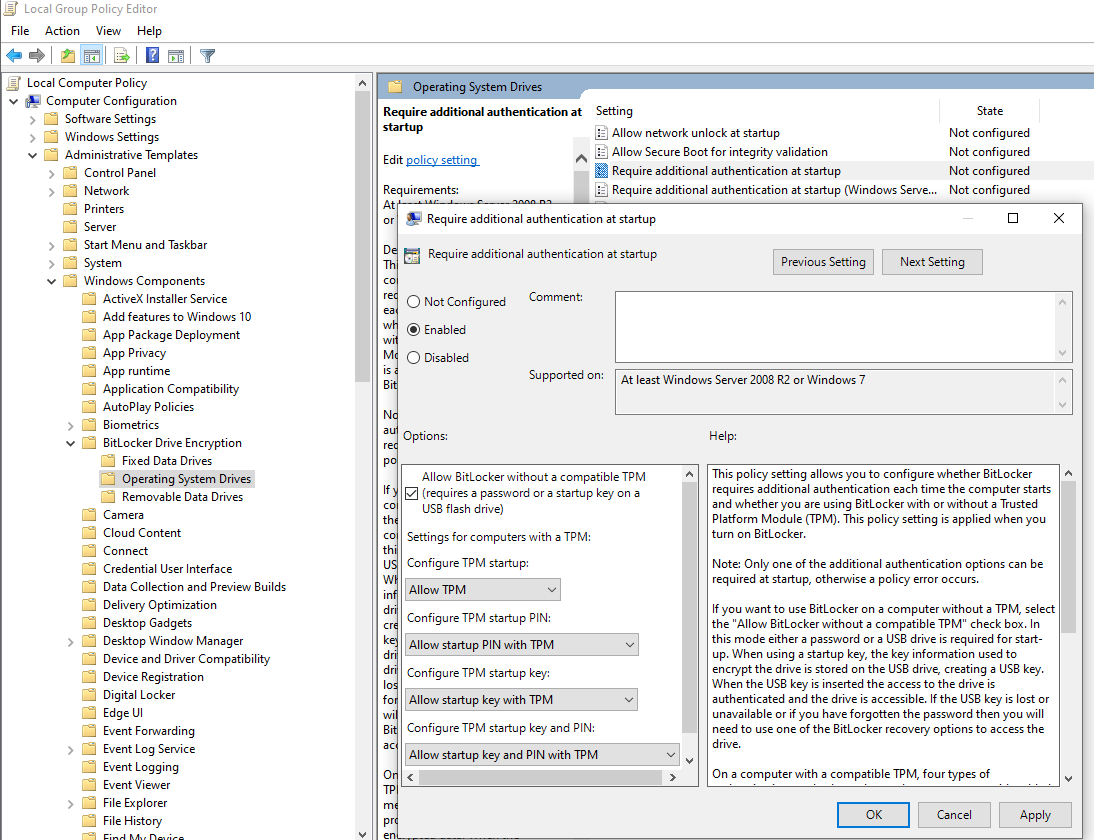 Navigate the Selection Tree and Enable the Options as Above
Navigate the Selection Tree and Enable the Options as Above
Proceeding with BitLocker configuration, you?ll be asked whether you?d like to insert a USB drive to prove your identity at startup or to enter a password. In this scenario, we?ll keep it simple and go with a password as you may be legally compelled to hand over a USB but not a password in some cases.
You?ll then be prompted to set up a recovery key in case you forget your password. You can either save it to your Microsoft account, save to a USB/external file or print it on paper. In our opinion, something on paper can be filed away from your computer so you?ll be able to retrieve it easily if you ever need it.
Finally, you?ll be asked whether BitLocker is being applied to a new installation or an existing Windows set up. The explanation is quite intuitive so we?re not going to regurgitate the explanation. Bottom line: If you?re reading this article from the computer you wish to encrypt, you?ll need to encrypt the whole drive.
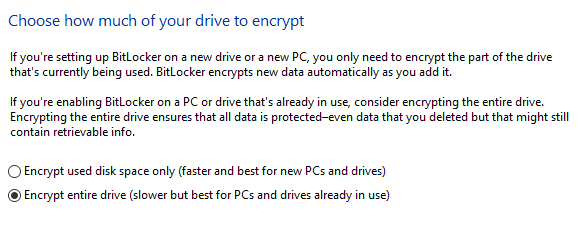 BitLocker Encryption Options
BitLocker Encryption Options
BitLocker will then begin encrypting your drive upon reboot. Congratulations, you?ve successfully configured PBA via BitLocker.
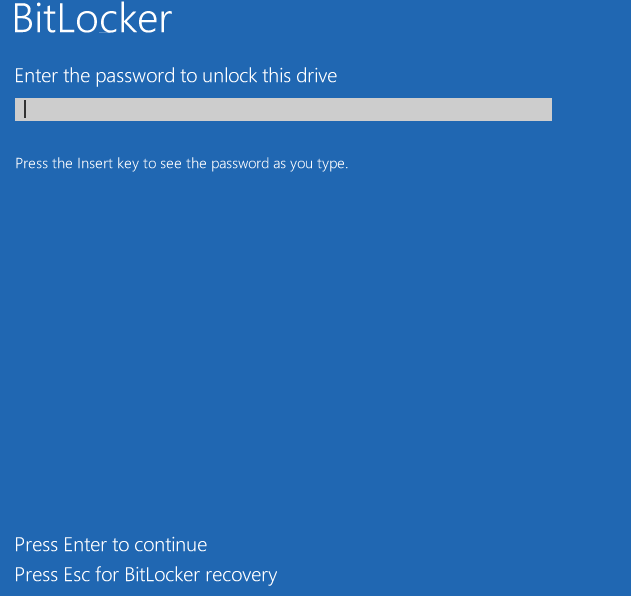 BitLocker Boot Prompt
BitLocker Boot Prompt
Encryption on macOS
Apple offers a built-in PBA FDE tool with its operating system (macOS 10.7 and higher): FileVault 2. This is the second generation of Apple?s encryption tool. The original FileVault (Referred to as Legacy FileVault) did not provide FDE and instead only encrypted the user Home directory.
For the remainder of this article, we will be referring to FileVault 2 as FileVault (It?s simpler that way!). FileVault utilises the AES-XTS symmetric encryption algorithm which relies on the same password for encryption and decryption. The data is split into 128-bit blocks encrypted by a 256-bit key.
FileVault can be found under Settings -> Security and Privacy -> FileVault and setup is quite straightforward. Make sure you record the master recovery key and keep it somewhere safe in case you forget your password one day.
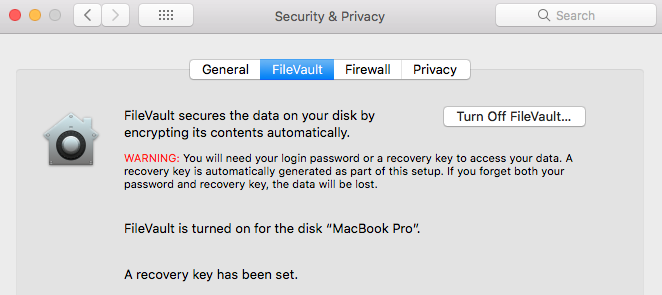 FileVault 2 Settings Page
FileVault 2 Settings Page
The only major drawback to this encryption method is that your master decryption password is your user password. Should someone obtain your password by phishing or another social engineering attack, they?ve got the keys to the kingdom. The password is also fixed which means that you?d need to decrypt and re-do the entire encryption setup with the new password should you require to change it.
Encryption on Linux
We?ve left the discussion on FDE options for Linux to last as it?s the most difficult to characterise generically due to the immense number of Linux distributions available in the wild. For today?s discussion, we?ll focus on the built-in PBA encryption implementation for Ubuntu.
The best bet is to do this with a fresh installation of Ubuntu. For this exercise, we?re using 18.04 LTS.
Ubuntu has always been one of the most user-friendly Linux installations so we won?t waste time and space in explaining the basic installation setup functions (It?s also very intuitive!). The important steps in the setup process for PBA FDE are illustrated below.
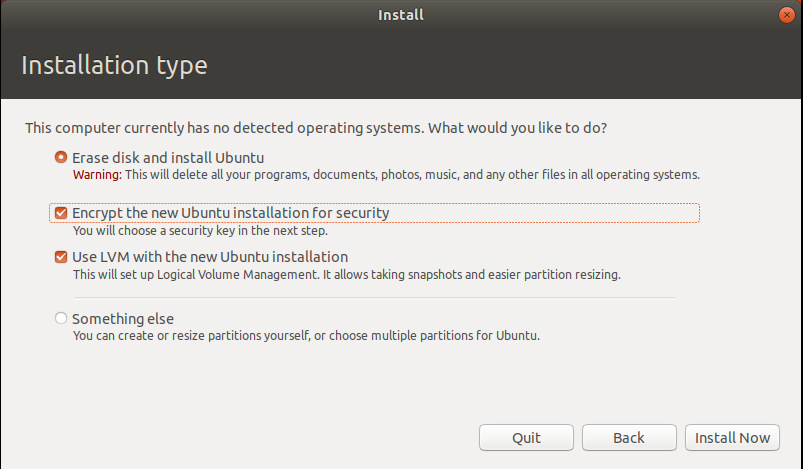 Encryption Option Enabled In Ubuntu Setup
Encryption Option Enabled In Ubuntu Setup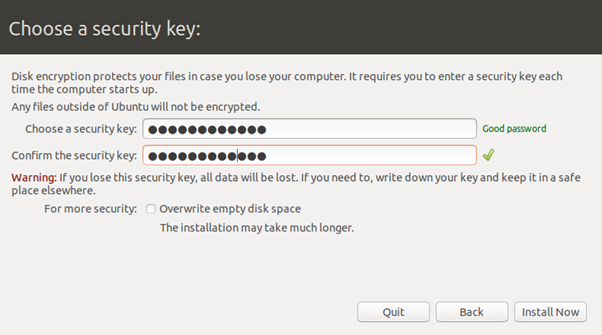 Password Setup
Password Setup
Make sure you enter a strong password. Unlike Apple?s FileVault, this password does not need to be your user account password. This will be an independent password. Just make sure you remember it!
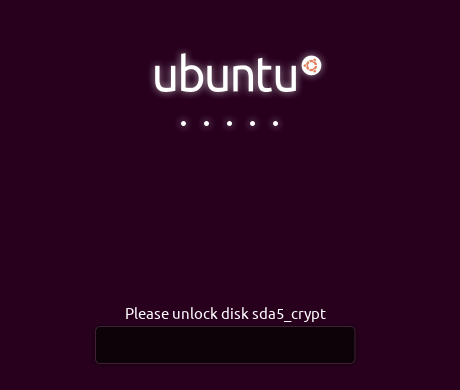 Ubuntu Decryption Boot Screen
Ubuntu Decryption Boot Screen
Nice and easy right? This is a heavily simplified approach to PBA FDE on Linux. Each distribution does encryption slightly differently. Be sure to consult the relevant help pages and forums for your distribution.
Final Thoughts
Although no form of encryption is considered ?unbreakable?, FDE intends to make the task of breaking your encrypted hard drive so painstakingly long that it is not considered worth the effort. No matter what your OS of choice is, there is an FDE method for you to assist with peace of mind when passing through customs.
FDE is also not a silver bullet. It should always be used in conjunction with other secure computing habits including good browser hygiene and password managers.
If you require assistance with setting up FDE on your machines, please feel free to get in contact with us. We?d be more than happy to provide some assistance.


