 Types of classification algorithms in Machine Learning
Types of classification algorithms in Machine Learning
In machine learning and statistics, classification is a supervised learning approach in which the computer program learns from the input data and then uses this learning to classify new observations. This data set may simply be bi-class (like identifying whether the person is male or female or that the mail is spam or non-spam) or it may be multi-class. Some practical examples of classification problems are: speech recognition, handwriting recognition, bio metric identification, document classification etc.
Here we have few types of classification algorithms in machine learning:
- Linear Classifiers: Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes Classifier
- Nearest Neighbor
- Support Vector Machines
- Decision Trees
- Boosted Trees
- Random Forest
- Neural Networks
Naive Bayes Classifier (Generative Learning Model) :
It is a classification technique based on Bayes? Theorem with the assumption of independence among predictors. In other words , a Naive Bayes classifiers assume that the presence of a particular feature in a class is unrelated to the presence of any other feature or that all of these properties have independent contribution to the probability. This family of classifiers is relatively easy to build and particularly useful for very large data sets as it is highly scalable. Along with simplicity, Naive Bayes is known to outperform even highly sophisticated classification methods.
Nearest Neighbor:
The k-nearest-neighbors algorithm is a supervised classification technique that uses proximity as a proxy for ?sameness?. The algorithm takes a bunch of labelled points and uses them to learn how to label other points. To label a new point, it looks at the labelled points closest to that new point (those are its nearest neighbors). Closeness is typically expressed in terms of a dissimilarity function. Once it checks with ?k? number of nearest neighbors, it assigns a label based on whichever label the most of the neighbors have.
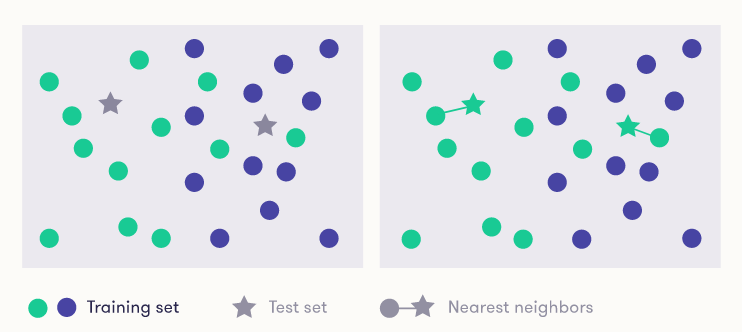
Using the geometric distance to decide which is the nearest item may not always be reasonable or even possible: the type of the input may, for example, be text, where it is not clear how the items are drawn in a geometric representation and how distances should be measured. You should therefore choose the distance metric on a case-by-case basis.
Logistic Regression (Predictive Learning Model) :
It is a statistical method for analyzing a data set in which there are one or more independent variables that determine an outcome. The outcome is measured with a dichotomous variable (in which there are only two possible outcomes). The goal of logistic regression is to find the best fitting model to describe the relationship between the dichotomous characteristic of interest (dependent variable = response or outcome variable) and a set of independent (predictor or explanatory) variables. This is better than other binary classification like nearest neighbor since it also explains quantitatively the factors that lead to classification.
Decision Trees:
Decision tree builds classification or regression models in the form of a tree structure. It breaks down a data set into smaller and smaller subsets while at the same time an associated decision tree is incrementally developed. The final result is a tree with decision nodes and leaf nodes. A decision node has two or more branches and a leaf node represents a classification or decision. The topmost decision node in a tree which corresponds to the best predictor called root node. Decision trees can handle both categorical and numerical data.
Random Forest:
Random forests or random decision forests are an ensemble learning method for classification, regression and other tasks, that operate by constructing a multitude of decision trees at training time and outputting the class that is the mode of the classes (classification) or mean prediction (regression) of the individual trees. Random decision forests correct for decision trees? habit of over fitting to their training set.
Neural Network:
A neural network consists of units (neurons), arranged in layers, which convert an input vector into some output. Each unit takes an input, applies a (often nonlinear) function to it and then passes the output on to the next layer. Generally the networks are defined to be feed-forward: a unit feeds its output to all the units on the next layer, but there is no feedback to the previous layer. Weightings are applied to the signals passing from one unit to another, and it is these weightings which are tuned in the training phase to adapt a neural network to the particular problem at hand.