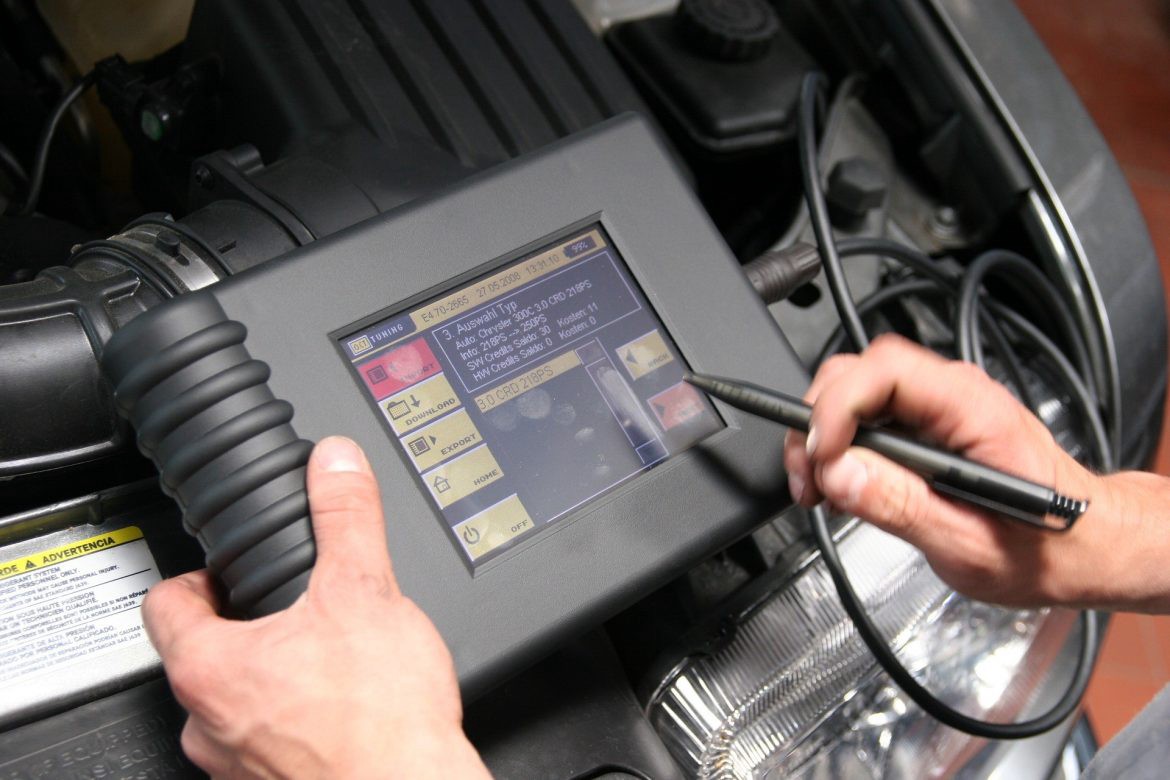
We?ve all been there. We are driving down the road and all of a sudden the check engine light goes on. Something is wrong with our car but what? The vehicle seems to be running fine. What is wrong? Before you take your vehicle into the auto repair and service shop, all you need to understand is that the computer is telling you something needs to get checked out. When you take your car for service the mechanic will run a diagnostic test with a scan tool to determine what is malfunctioning.
On Board Diagnostics (OBD-II) is an automotive term referring to a vehicle?s self-diagnostic and reporting capability. When your check engine light, called a Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL), goes on it means your vehicle has one or more OBD-II trouble codes.
The OBD systems came from California?s strict smog emission control standards that started in 1966 model cars that were required to implement emissions control systems. The federal government extended these controls nationwide in 1968. OBD-II detects a problem with your car that could cause your vehicle?s emissions to exceed 1.5 times the legal limit.
The trouble code, or diagnostic code, is an alphanumeric value that corresponds to a particular problem. The codes were created by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) to comply with OBD-II emissions regulations in the US.
Diagnostic codes are divided into four categories: Powertrain (P), Body (B), Chassis and Network Communications (U). The codes are further divided into two major groups: Generic or global (0 as second digit) and enhanced or manufacturer specific (1 as second digit).
Here are the five most common diagnostic codes you will likely experience at some point during the lifespan of your vehicle.
1. OXYGEN SENSOR
CODES: PO171-P0175

One of the most common car problems involves a faulty oxygen sensor. A vehicle?s oxygen sensor monitors the amount of oxygen in the exhaust so the engine computer can adjust the fuel mixture to maximize fuel economy and minimize emissions. If your oxygen sensor isn?t working properly, your gas mileage will increase or in some cases your car will randomly stall.
2. ENGINE MISFIRE
CODES: P0300-P0305

Mechanics work on engine misfires on a daily basis. If your engine is misfiring it means that one or more of the cylinders isn?t working properly. If your car is vibrating or shaking while idling and your car isn?t as fuel efficient as it should be, then you might have an engine misfire problem. The OBD-II system tracks engine misfires by monitoring the speed of the crankshaft when the engine is running. The OBD-II system logs a misfire when it detects a slight loss of speed in the crankshaft.
3. EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM
CODES: P0411, P0440, P0442, P0446, P0455

The evaporation system (EVAP) is responsible for containing and removing vapors that are produced when fuel is burned. A loose gas cap allowing fuel vapors to escape from the fuel tank can often be the reason for setting off this trouble code. EVAP includes vent hoses, a charcoal canister, a purge valve and a pressure or vacuum sensor.
4. EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
CODE: P0401

The exhaust gas recirculation, commonly known as EGR, controls the engine?s emission of smog-causing nitrous oxides (NOx). EGR recirculates part of an engine?s exhaust gas back to the engine cylinders. The car?s computer system opens and closes valves to recirculate the engine?s exhaust gas. Problems occur if the oil hasn?t been changed in a while or the car takes many short trips because the car isn?t allowed enough time to warm up, causing carbon buildup.
5. CATALYTIC CONVERTER
CODE: P0420, P0430

The downstream oxygen sensor monitors the catalytic converter. According to Wikipedia, the catalytic converter is ?an emissions control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas to less toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction (an oxidation and a reduction reaction).? The converter can become contaminated and increase tailpipe emissions if the engine is burning oil or leaking coolant internally or is worn out from age.
Next time the engine light turns on you should feel confident knowing that it is likely one of these emissions control codes. Get your car serviced at a certified auto repair and service shop through the CAKNOW mobile app platform and make sure your car is running smoothly and not polluting the environment.
Resources
Links:
http://affordableautohopkins.com/four-common-car-diagnostic-codes
http://www.aa1car.com/library/common_trouble_codes.htm
http://www.trouble-codes.com/
http://www.obdii.com/background.html
https://www.engine-light-help.com/oxygen-sensor-codes.html