
What is Whey Protein?
Along with casein, whey is one of the two types of protein found in cow?s milk. Unlike casein, whey is a fast-digesting protein but it only makes up about 20% of the protein found in milk.
Whey is a complete protein, meaning it contains all 9 essential amino acids, and has a considerably well-balanced amino acid profile, making it ideal for everything from bodybuilding to weight loss.
On top of being the most popular dietary supplement in the world, whey is also amongst the most well-researched. But there are a few different forms of whey protein and each goes through their own unique series of processing.
It?s through this processing that the nutritional profiles of each protein begin to diverge. The two types of whey protein most commonly found in dietary supplements are whey isolate and whey concentrate.

What?s the Difference Between Whey Isolate & Whey Concentrate?
The biggest difference between whey isolate and whey concentrate has to do with the amount of filtering that each goes through. Whey isolate goes through significantly more processing than whey concentrate, which means that each scoop of isolate ultimately contains more actual protein at the end of the day.
1. Whey Isolate Has A Higher Protein Content
After it?s separated from milk, whey isn?t just made up of proteins, it also contains carbohydrates and fats. Because it goes through less processing, whey concentrate ultimately has more fat and carbs compared to isolate ? more fat and carbs means less protein per scoop.
Although, it?s important to point out that even amongst different concentrates, the amount of processing varies and as a result, so does the overall protein content.
In general, the protein content of different whey concentrates can range anywhere from about 30% to around 80%. On the other hand, whey isolates are usually at least 90% pure protein, with the purest forms coming it closer to 95%. At the end of the day, that means each scoop of isolate contains more actual protein.
2. Whey Isolate Has Less Lactose
Because of the extra processing, it goes through, whey isolate has a very low lactose content. Lactose is a carbohydrate -it?s a sugar ? and the vast majority of carbs are extracted during processing.
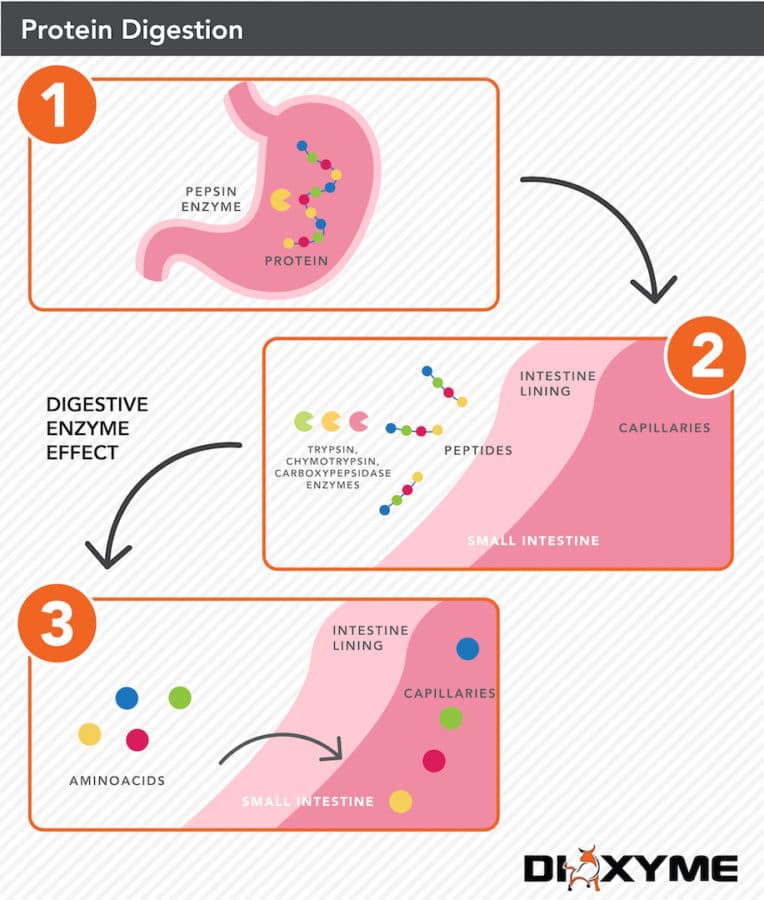
In fact, many people who are lactose intolerant are actually able to consume whey isolate without issue.
It should be noted however that although it doesn?t go through as much processing, whey concentrate still has a pretty low lactose content, meaning that it likely won?t affect those with less severe cases of lactose intolerance.
Some whey protein products also have digestive enzymes added to them, which in addition to helping with absorption, also aid in breaking down whatever lactose is present.
3. Whey Isolate Is More Expensive
One of the most obvious differences between whey isolate and whey concentrate is the price.
Because there?s more processing involved, it ultimately costs more to produce isolate, which means that products containing only pure isolate are usually going to be more expensive. However, with that being said, many whey protein products ultimately contain a mixture of both isolate and concentrate.
4. Whey Concentrate Has a Slightly Lower Biological Value
Biological value (BV) is a common method scientists use to measure the quality of a protein. In basic terms, BV measures how much of the protein actually gets used up by your body in the production of new tissues. The higher the biological value, the better the protein source.
Both whey isolate and whey concentrate have very high biological values. In fact, whey concentrate has a similar biological value to an egg, which has the highest BV of any natural whole food ? whey concentrate has a BV of 104 compared to an egg?s BV of 100.
While whey concentrate?s biological value is impressive in its own right, whey isolate?s is even higher. In fact with a BV of 140+, whey isolate currently has the highest biological value of any protein source scientists have measured.
5. Whey Isolate Is Absorbed at a Faster Rate
While your body is ultimately efficient with both forms of protein, they?re absorbed at different rates. Following consumption, whey isolate is rapidly absorbed, usually reaching the bloodstream in around an hour. Whey concentrate on the other hand usually takes between 2?3 hours before your body can start to use it.
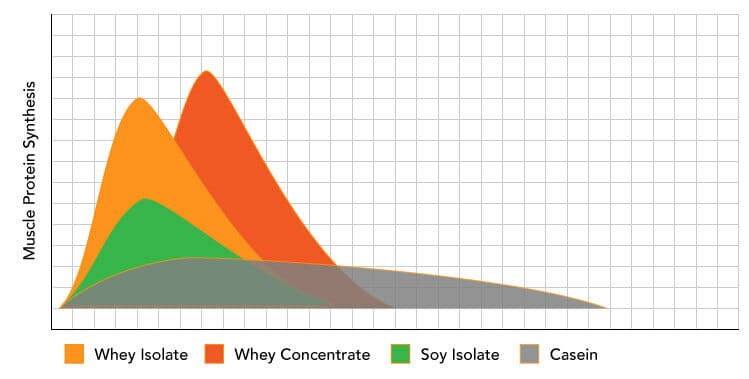
6. Whey Concentrate Produces A Greater Spike in Muscle Protein Synthesis
Muscle protein synthesis (MPS) is the main mechanism through which your muscle tissues are rebuilt. In simple terms, MPS is a coordinated process through which your body arranges for the delivery of nutrients to muscle cells in need of repair.
While both whey isolate and concentrate produce significant spikes in MPS following consumption, research shows that whey concentrate may trigger MPS to an even greater degree than whey isolate.
7. Whey Concentrate Contains Immunoglobulins and Bioactive Peptides
During the additional processing that it goes through, immunoglobulins (IGs) and bioactive peptides (BPs) are removed from whey isolate. They might sound like bad things but IGs and BPs actually play a critical role in liver, lipid, bone, and heart health.
Whey Protein Isolate vs Concentrate: Which One is Right for You?
The truth of the matter is that the differences between whey isolate and whey concentrate are relatively minuscule when we?re looking at the bigger picture. Each form has a high biological value and fast absorption rate and both produce significant spikes in muscle protein synthesis.
However as we just discussed, there are some things that set whey isolate and concentrate apart from one another and as such, each may be better suited for some goals and less so for others.
But again, it?s important to point out that at the end of the day, supplementing with whey protein can be beneficial for your health no matter which form you choose.
Which One is Better For Overall Health?
If you?re supplementing with whey protein mainly for health-related purposes, whatever they may be, whey concentrate could be the better option.
While concentrate may contain less actual protein per scoop, it?s packed full of immunoglobulins and bioactive peptides, which play an important role in everything from regulating lipid levels to maintaining bone mineral density.
Which One is Better For Weight Loss?
Chances are if you?re supplementing with protein during a weight cut, it?s because you?re looking for just that ? protein. While restricting your carbs and/or fat during a weight cut is a must, you still need to consume a lot of protein if you want to lose fat and not muscle.
That?s why many people on a weight loss diet chose to go with whey isolate ? it?s 90+% protein, which means your not getting all of the carbs and fat that are still present in whey concentrate. Now, in reality, there are not that many extra calories in whey concentrate but when you?re trying to lose weight, every calorie counts.
Which One is Better for Building Muscle?
When it comes to packing on size and strength, muscle protein synthesis (MPS) is key ? again, it?s the main mechanism through which your muscles actually grow. Because each form of protein triggers MPS in slightly different ways, it can be advantageous to combine both whey isolate and concentrate if your goal is building muscle. In fact, a number of whey protein products actually mix the two together for this very purpose.

Whey isolate?s rapid absorption rate produces a quick spike in muscle protein synthesis, which is perfect post-workout where your muscles are most in need of nutrients. But whey concentrate ultimately produces a greater spike in MPS over a longer period of time, which can help supply your muscles with the nutrients they need longer after your workout.
Wrap Up
Whey isolate and whey concentrate are both excellent sources of protein; however, each goes through different amounts of processing and as a result, each has a slightly different nutritional profile.
Whey concentrate has a higher lactose content and also contains more carbs and fat, while whey isolate is usually over 90% pure protein. They also have different biological values and absorption rates.
While both forms of whey protein are beneficial, each may be particularly well-suited for certain goals. Whey concentrate may be a good choice for those looking to save money and support their overall health.
Whey isolate, on the other hand, is an excellent choice for those interested in weight loss and/or limiting their lactose consumption.
References
- ?Protein ? Which is Best?? Hoffman, J.R. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine. Sep. 2004.
- ?The impact of protein quality on the promotion of resistance exercise-induced changes in muscle mass? Phillips, S.M. Nutrition and Metabolism. Sep. 2016.
- ?Protein ? Which is Best?? Hoffman, J.R. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine. Sep. 2004.
- ?Protein ? Which is Best?? Hoffman, J.R. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine. Sep. 2004.
- ?Protein quality assessment: impact of expanding understanding of protein and amino acid needs for optimal health.? Millward, D.J., Layman, D.K., Tome, D., Schaafsma, G. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. May. 2009.
- ?Whey protein concentrates and isolates: Processing and functional properties? Morr, C.V., Ha, E.Y. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 1993.
- ?Whey and whey proteins-From ?gutter-to-gold?? Smithers, G.W. International Dairy Journal. Jul. 2008.
A combination of both whey isolate and whey concentrate may be especially advantageous for those looking to build size and strength.
Originally published at https://dioxyme.com on August 26, 2019.


