 Gini index doesn?t commit the logarithm function and picks over Information gain, learn why Gini Index can be used to split a decision tree.
Gini index doesn?t commit the logarithm function and picks over Information gain, learn why Gini Index can be used to split a decision tree.
Beginning with Data mining, a newly refined one-size-fits approach to be adopted successfully in data prediction, it is a propitious method used for data analysis to discover trends and connections in data that might cast genuine interference.
Some popular tools operated in Data mining are artificial neural networks(ANN), logistics regression, discriminant analysis, and decision trees.
The decision tree is the most notorious and powerful tool that is easy to understand and quick to implement for knowledge discovery from huge and complex data sets.
Introduction
The number of theoreticians and practitioners are regularly re-polishing techniques in order to make the process more rigorous, adequate and cost-effective.
Initially, decision trees are used in decision theory and statistics on a large scale. These are also compelling tools in Data mining, information retrieval, text mining, and pattern recognition in machine learning.
Here, I would recommend reading my previous article to dwell and sharpen your knowledge pool in terms of decision trees.
The essence of decision trees prevails in dividing the data sets into its sections which indirectly emerging a decision tree (inverted) having roots nodes at top. The stratified model of the decision tree leads to the end result through the pass over nodes of the trees.
Here, each node comprises an attribute (feature) that becomes the root cause of further splitting in the downward direction.
Can you answer,
- How to decide which feature should be located at the root node,
- Most accurate feature to serve as internal nodes or leaf nodes,
- How to divide tree,
- How to measure the accuracy of splitting tree and many more.
There are some fundamental splitting parameters to address the considerable issues discussed above. And yes, in the realm of this article, we will cover the Entropy, Gini Index, Information Gain and their role in the execution of the Decision Trees technique.
During the process of decision making, multiple features participate and it becomes essential to concern the relevance and consequences of each feature thus assigning the appropriate feature at the root node and traversing the splitting of nodes downward.
Moving towards the down direction leads to decreases in the level of impurity and uncertainty and yields in better classification or elite split at each node.
To resolve the same, splitting measures are used like Entropy, Information Gain, Gini Index, etc.
Defining Entropy
?What is entropy?? In the Lyman words, it is nothing just the measure of disorder, or measure of purity. Basically, it is the measurement of the impurity or randomness in the data points.
A high order of disorder means a low level of impurity, let me simplify it. Entropy is calculated between 0 and 1, although depending upon the number of groups or classes present in the data set it could be larger than 1 but it signifies the same meaning, i.e. higher level of disorder.
For the sake of simple interpretation, let us confine the value of entropy between 0 and 1.
In the below image, an inverted ?U? shape depicts the variation of entropy on the graph, the x-axis presents data points and the y-axis shows the value of entropy. Entropy is the lowest (no disorder) at extremes (both end) and maximum (high disorder) in the middle of the graph.
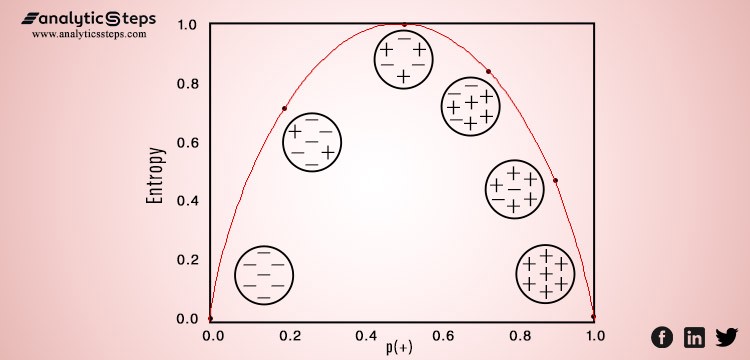 Variation of entropy against data points
Variation of entropy against data points
?Entropy is a degree of randomness or uncertainty, in turn, satisfies the target of Data Scientists and ML models to reduce uncertainty.?
What is Information Gain?
The concept of entropy plays an important role in calculating Information Gain.
Information Gain is applied to quantify which feature provides maximal information about the classification based on the notion of entropy, i.e. by quantifying the size of uncertainty, disorder or impurity, in general, with the intention of decreasing the amount of entropy initiating from the top (root node) to bottom(leaves nodes).
The information gain takes the product of probabilities of the class with a log having base 2 of that class probability, the formula for Entropy is given below:
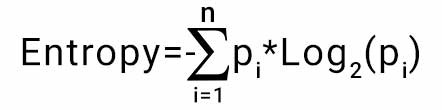 Entropy Formula
Entropy Formula
Here ?p? denotes the probability that it is a function of entropy.
Gini Index in Action
Gini Index, also known as Gini impurity, calculates the amount of probability of a specific feature that is classified incorrectly when selected randomly. If all the elements are linked with a single class then it can be called pure.
Let?s perceive the criterion of the Gini Index, like the properties of entropy, the Gini index varies between values 0 and 1, where 0 expresses the purity of classification, i.e. All the elements belong to a specified class or only one class exists there. And 1 indicates the random distribution of elements across various classes. The value of 0.5 of the Gini Index shows an equal distribution of elements over some classes.
While designing the decision tree, the features possessing the least value of the Gini Index would get preferred. You can learn another tree-based algorithm(Random Forest).
The Gini Index is determined by deducting the sum of squared of probabilities of each class from one, mathematically, Gini Index can be expressed as:
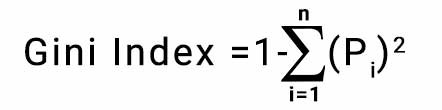 Gini Index Formula
Gini Index Formula
Where Pi denotes the probability of an element being classified for a distinct class.
Classification and Regression Tree (CART) algorithm deploys the method of the Gini Index to originate binary splits.
In addition, decision tree algorithms exploit Information Gain to divide a node and Gini Index or Entropy is the passageway to weigh the Information Gain.
Gini Index vs Information Gain
Take a look below for the getting discrepancy between Gini Index and Information Gain,
- The Gini Index facilitates the bigger distributions so easy to implement whereas the Information Gain favors lesser distributions having small count with multiple specific values.
- The method of the Gini Index is used by CART algorithms, in contrast to it, Information Gain is used in ID3, C4.5 algorithms.
- Gini index operates on the categorical target variables in terms of ?success? or ?failure? and performs only binary split, in opposite to that Information Gain computes the difference between entropy before and after the split and indicates the impurity in classes of elements.
Conclusion
Gini index and Information Gain are used for the analysis of the real-time scenario, and data is real that is captured from the real-time analysis. In numerous definitions, it has also been mentioned as ?impurity of data? or ? how data is distributed. So we can calculate which data is taking less or more part in decision making.
Today I end up with our top reads:
- When Artificial Intelligence (AI) And Neuroscience Meet
- How Instagram Uses AI and Big Data Technology?
- How Tesla is making use of Artificial Intelligence in its operations?
- Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) in Unsupervised Machine Learning
- TensorFlow Tutorial: From Introduction to Applications
Oh great, you have made it to the end of this blog! Thank you for reading!!!!!

