JavaScript?s location object
 Location CheatSheet.
Location CheatSheet.
You can use the window.location property to access the URL of the current page .
If you want to go to a new page , either you can change the href property of history object or call assign method with new url as argument.
location.href = “new url”;// or we can use location.assign(“new url”);
For redirecting without storing in history:
location.replace(“new url”);
For reloading the page:
window.location.reload()
Force refresh
We can pass true to force the reloaded page to come from the server (instead of the cache). Alternatively, we can use false to reload the page from the cache.
//from cachewindow.location.reload(); window.location.reload(false);// from serverwindow.location.reload(true);
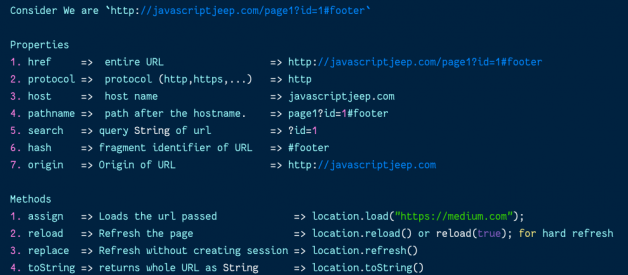
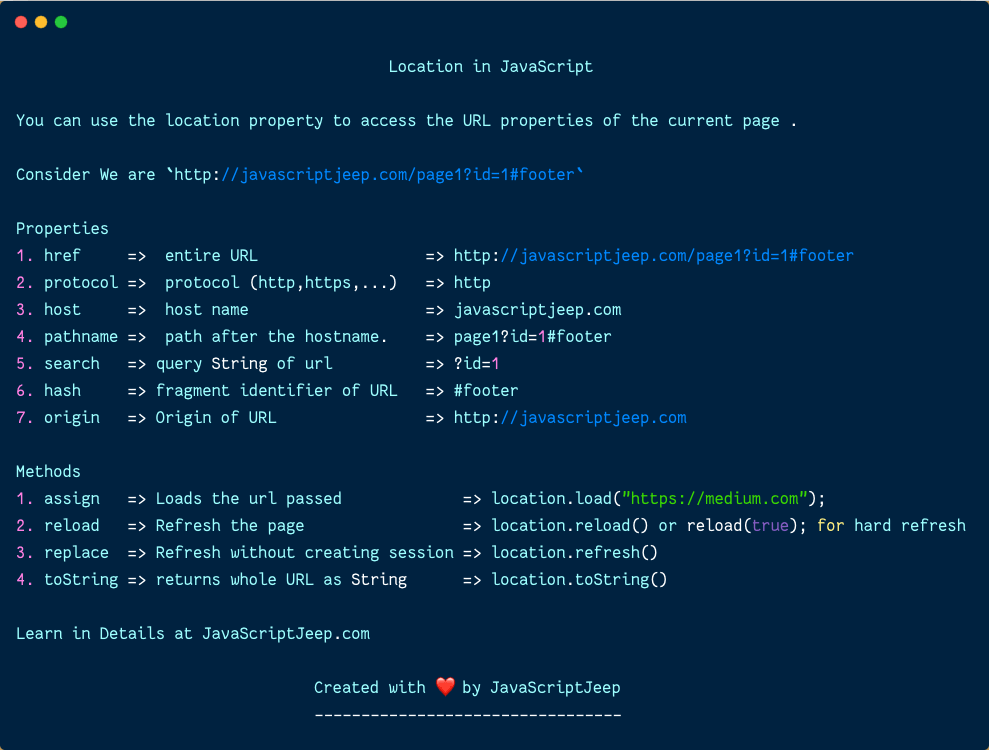
Properties of Location Object
1. Href
Contains the entire URL of the page.
location.href; // current page url addresss
When we assign a new value to the property, it will redirect the url value set to the property.
location.href = “https://google.com”;
Make sure to add http/https. Otherwise, it makes the request on the same page.
2. Protocol
Contains the protocol (http,https,…) of the page.
location.protocol; // https:
3. Host
Website hostname with port number.
location.host; // medium.com // with port number var anchor = document.createElement(“a”);anchor.href = “https://medium.com:4097anchor.host // “medium:4097”
4. Hostname
Website hostname.
location.host; // medium.com
5. Port
Contains the port number. If the URL does not contain an explicit port number, it will be set to ”.
var anchor = document.createElement(“a”);anchor.href = “https://medium.com:4097anchor.port // “4097”
6. Pathname
Contains the path after the hostname.
location.href; //https://medium.com/@jagathishsaravananlocation.pathname; // “/@jagathishsaravanan”
7. Search
Returns the search part of URL.
I am on page https://medium.com/search?q=javascriptjeep;location.search; // ?q=javascriptjeep
8. Hash
Contains string of ‘#’ followed by the fragment identifier of the URL. This will be useful when we have links inside the same page.
Example from MDN Web Docs:
<a id=”myAnchor” href=”/en-US/docs/HTMLHyperlinkElementUtils.href#Examples”>Examples</a><script> var anchor = document.getElementById(“myAnchor”); console.log(anchor.hash); // Returns ‘#Examples'</script>
9. Origin
Origin of specific location.
consider we are at page : https://medium.com/search?q=javascriptjeeplocation.origin; // https://medium.com
Methods
1. assign
Loads the resource at the URL provided in the parameter.
location.assign(“https://medium.com”);
This will redirect to medium.com.
2. reload
The Location.reload() method reloads the current URL, like the Refresh button.
location.reload();
It has an optional parameter forceReload, which defaults to false when forceReload is true. Then it loads the page from the server, instead of loading from the browser cache.
location.reload(true);
3. replace
Replaces the current resource with the one at the provided URL.
// consider we are google.com// when we run this line location.replace(“htts://medium.com”)// it will replace the current page and redirect to medium page
The difference from the assign() method is that after using replace(), the current page will not be saved in session History, meaning the user won’t be able to use the Back button to navigate to it.
4. toString
Returns the whole URL as a string.
location.toString();// https://medium.com/search?q=javascriptjeep
Reference: MDN Web Docs.
Follow Javascript Jeep??