Oracle Database is an object-relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Oracle Corporation. The Oracle Database 12c is a high-performance, enterprise-class database. Oracle Database is the most popular, trusted database systems. Oracle Database supports multiple operating systems like Redhat, SUSE, Oracle Linux, Microsoft Windows, and IBM Linux.

In this article, we will explain how to install Oracle Database 12c on Linux Server.
Step 1: Prerequisites
Packages: First, we need to install the required packages. These packages we can easily get from OS officially repository.
# yum install -y binutils.x86_64 compat-libcap1.x86_64 gcc.x86_64 gcc-c++.x86_64 glibc.i686 glibc.x86_64 glibc-devel.i686 glibc-devel.x86_64 ksh compat-libstdc++-33 libaio.i686 libaio.x86_64 libaio-devel.i686 libaio-devel.x86_64 libgcc.i686 libgcc.x86_64 libstdc++.i686 libstdc++.x86_64 libstdc++-devel.i686 libstdc++-devel.x86_64 libXi.i686 libXi.x86_64 libXtst.i686 libXtst.x86_64 make.x86_64 sysstat.x86_64 zip unzip
Host File: The host file must contain a fully qualified name for the server.
127.0.0.1 oracle.techoism.net oracle192.168.1.110 oracle.techoism.net oracle
Selinux: Set secure Linux to permissive using selinux configuration file.
# vim /etc/sysconfig/selinx
Change the parameters.
SELINUX=permissive
Reboot the server or execute the mentioned command.
# setenforce Permissive
IPTables: If on server Linux firewall is enabled, so you need to stop it and need to configure it.
For CentOS/RHEL 7# systemctl stop firewalld# systemctl disable firewalldFor CentOS/RHEL 6# service iptables stop# chkconfig iptables off
Step 2: Create User and Group
Oracle database will run with a normal Linux user. So we need to create the user and group for Oracle.
# groupadd oinstall# groupadd dba# useradd -g oinstall -G dba oracle
Set the oracle user password.
# passwd oracle
Step 3: Kernel Parameters
Now we need to configure our system before starting the installation of Oracle Database. Add mention kernel parameters in sysctl.conf file.
# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
Add the mention lines.
fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576fs.file-max = 6815744kernel.shmall = 2097152kernel.shmmax = 8329226240kernel.shmmni = 4096kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 9000 65500net.core.rmem_default = 262144net.core.rmem_max = 4194304net.core.wmem_default = 262144net.core.wmem_max = 1048586
Reload the configuration file to reflect the changes.
# sysctl -p# sysctl -a
Next, we need to configure some limits for the oracle user.
# vim /etc/security/limits.conforacle soft nproc 2047oracle hard nproc 16384oracle soft nofile 1024oracle hard nofile 65536oracle soft stack 10240oracle hard stack 32768
Step 4: Configure X11 Forwarding
X11 forwarding refers to executing such a program remotely through an SSH (Secure Shell) connection. With X11 you can easily install the Oracle Database. You can use mention link to configure X11 on the server.
X11 Configuration
Step 5: Create the Directories
Before installing Oracle Database, create directories that will be used during the Oracle installation, and provide the required permissions.
# mkdir /u01# chown -R oracle:oinstall /u01# chmod -R 775 /u01# chmod g+s /u01
Step 6: Extract the File
Once you will download the Oracle database setup from Oracle official website. Extract the Oracle files on a Linux server.
# cd /software# unzip linuxx64_12201_Oracle_database.zip
Step 7: Install Oracle Database
Start the Oracle Database Installer issuing the following command in the database directory.
# cd /software/database# ./runInstaller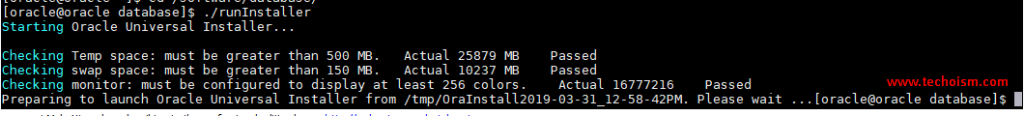
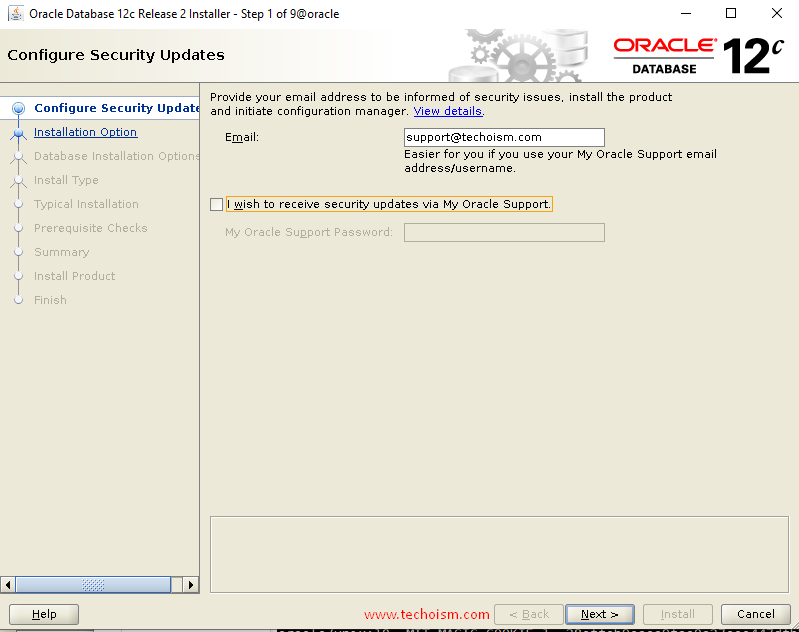
Provide your email address to be informed of security issues and click ?Enter?
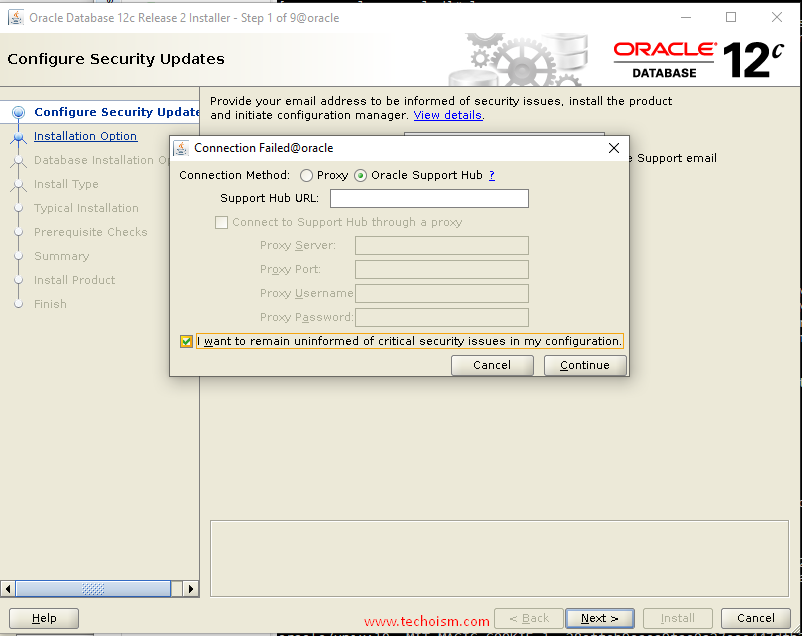
If you are using any proxy server then provide the details of the proxy server and click ?Continue?
Choose create and configure a database option and click ?Next?
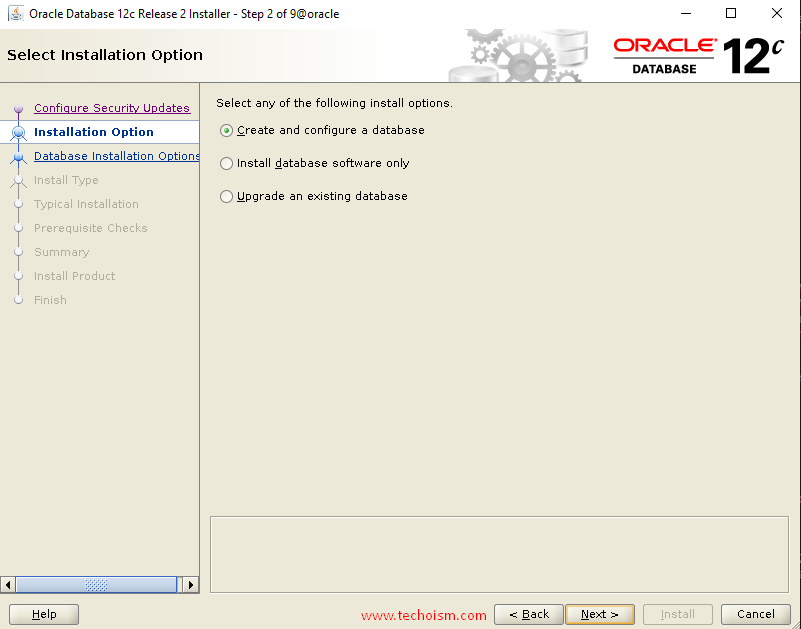
Under the ?System Class? section, choose system class and click ?Next? again.

In this section, Select the type of installation you want to select and click ?Next?
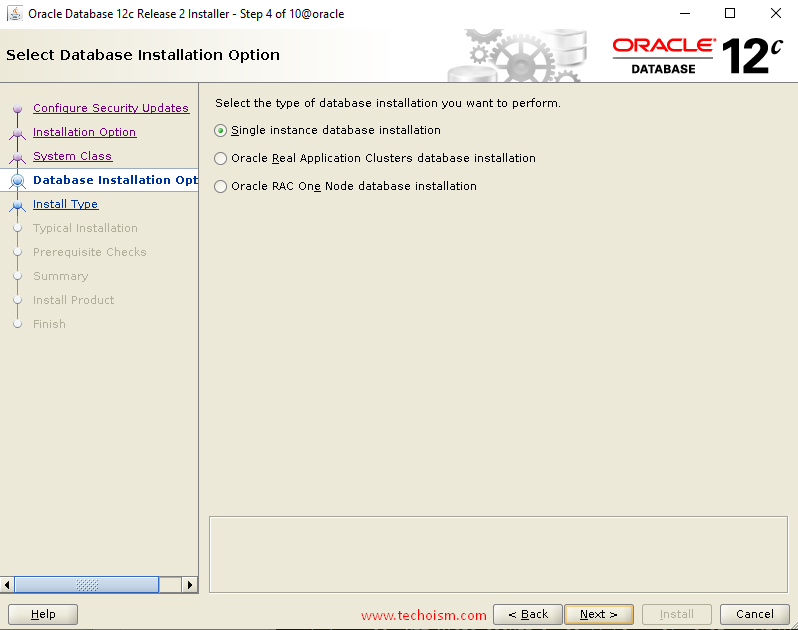
Select the installation type and click ?Next?

Now specify full database installation with basic configuration and click ?Next?
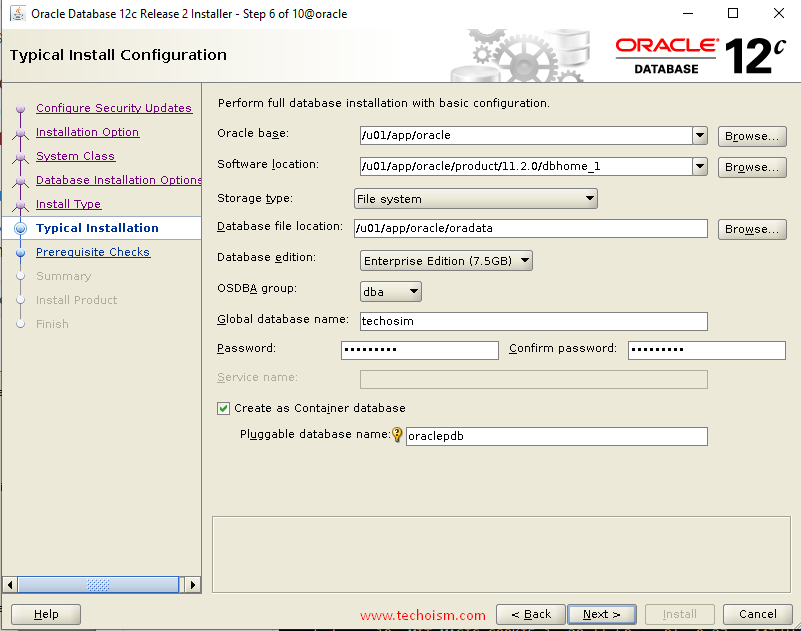
You are starting your first installation on the host. Specify a directory for Installation metadata files and click ?Next?
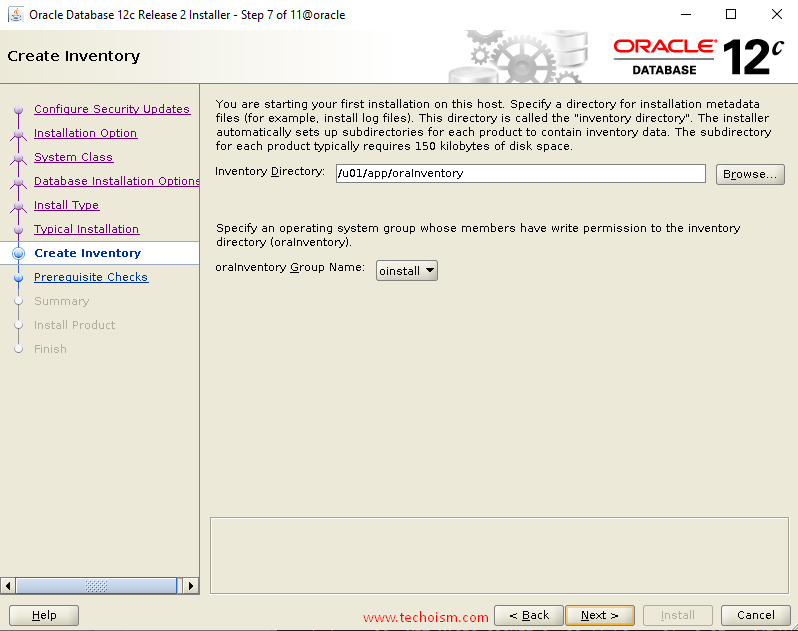
Verify that the installation pre-checks are completed without errors. then it will show the summary of the information such as global settings, database information, etc. Review the information and click ?install?.
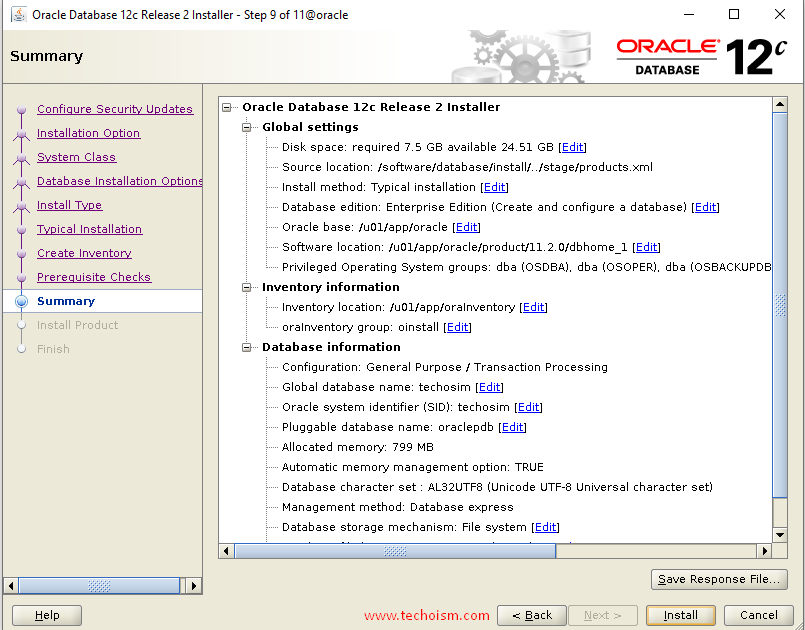
Now the installation of Oracle Database has been started. It will take a few minutes to complete.

During the installation, you need to run a couple of scripts to set the required permissions.
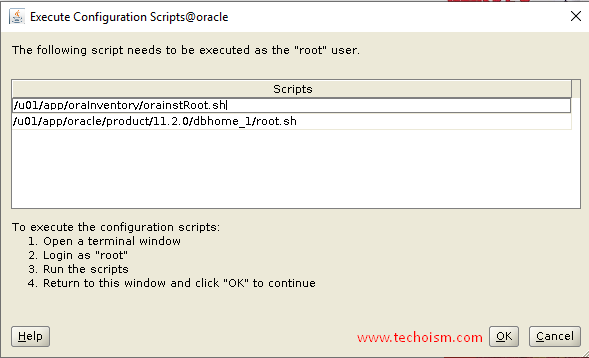 # /u01/app/oraInventory/orainstRoot.shChanging permissions of /u01/app/oraInventory.Adding read,write permissions for group.Removing read,write,execute permissions for world.Changing groupname of /u01/app/oraInventory to oinstall.The execution of the script is complete.# /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1/root.shPerforming root user operation. The following environment variables are set as: ORACLE_OWNER= oracle ORACLE_HOME= /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1 Enter the full pathname of the local bin directory: [/usr/local/bin]: Copying dbhome to /usr/local/bin … Copying oraenv to /usr/local/bin … Copying coraenv to /usr/local/bin … Creating /etc/oratab file… Entries will be added to the /etc/oratab file as needed by Database Configuration Assistant when a database is created Finished running generic part of root script. Now product-specific root actions will be performed. Do you want to setup Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA) now ? yes|[no] : Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA – User Mode) is available at : /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1/suptools/tfa/release/tfa_home/bin/tfactl OR Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA – Daemon Mode) can be installed by running this script : /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1/suptools/tfa/release/tfa_home/install/roottfa.sh
# /u01/app/oraInventory/orainstRoot.shChanging permissions of /u01/app/oraInventory.Adding read,write permissions for group.Removing read,write,execute permissions for world.Changing groupname of /u01/app/oraInventory to oinstall.The execution of the script is complete.# /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1/root.shPerforming root user operation. The following environment variables are set as: ORACLE_OWNER= oracle ORACLE_HOME= /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1 Enter the full pathname of the local bin directory: [/usr/local/bin]: Copying dbhome to /usr/local/bin … Copying oraenv to /usr/local/bin … Copying coraenv to /usr/local/bin … Creating /etc/oratab file… Entries will be added to the /etc/oratab file as needed by Database Configuration Assistant when a database is created Finished running generic part of root script. Now product-specific root actions will be performed. Do you want to setup Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA) now ? yes|[no] : Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA – User Mode) is available at : /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1/suptools/tfa/release/tfa_home/bin/tfactl OR Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA – Daemon Mode) can be installed by running this script : /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1/suptools/tfa/release/tfa_home/install/roottfa.sh
Oracle database configuration has been completed and clicks ?Next?.

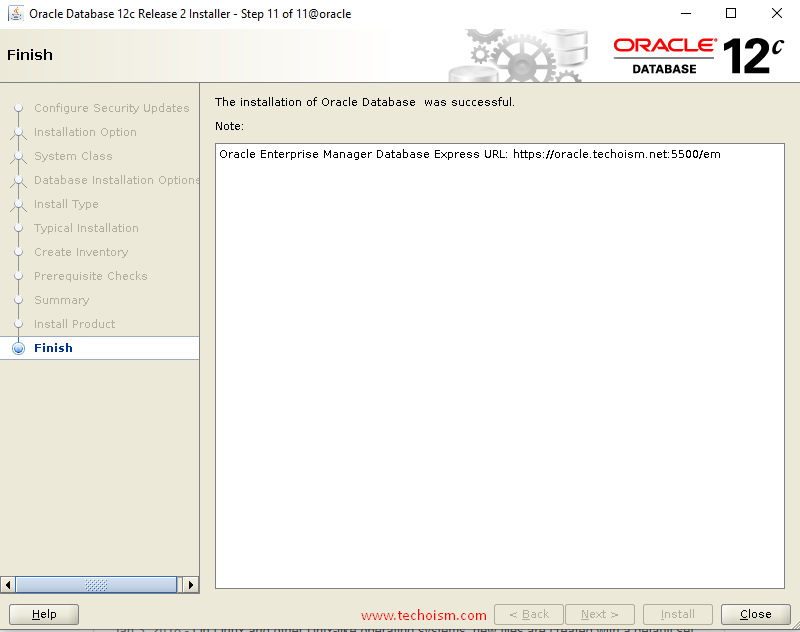
Step 8: Access Oracle Enterprise Manager
When it is finished, you will be presented with the message indicating the URL of the Oracle Enterprise Manager:
https://oracle.techoism.net:5500/em
Step 10: Set Oracle Home Directory
Add the following lines in the user home directory at .bash_profile file.
# su – oracle# vim .bashrcTMPDIR=$TMP; export TMPDIRORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle; export ORACLE_BASEORACLE_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/12.1.0/dbhome_1; export ORACLE_HOMEORACLE_SID=techoism; export ORACLE_SIDPATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH; export PATHLD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/lib:/lib:/usr/lib:/usr/lib64; export LD_LIBRARY_PATHCLASSPATH=$ORACLE_HOME/jlib:$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/jlib; export CLASSPATH
Execute the mentioned command.
# source .bash_profile
Step 11: Listener File Configuration
Finally, replace the host in the listener.ora file.
# vim $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/listener.ora
Find the below parameter.
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = oracle.techoism.net)(PORT = 1521)
Change the parameter with 0.0.0.0
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = 0.0.0.0)(PORT = 1521)
Step 12: Enabling Oracle to Start on System Boot
To enable the database service to start automatically on boot, create the service file for the Oracle database and add the mention lines.
# vim /etc/systemd/system/oracle-rdbms.service#/etc/systemd/system/oracle-rdbms.service#Invoking Oracle scripts to start/shutdown Instances defined in /etc/oratab #and starts Listener[Unit]Description=Oracle Database(s) and ListenerRequires=network.target[Service]Type=forkingRestart=noExecStart=/u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1/bin/dbstart /u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1ExecStop=/u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1/bin/dbshut /u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1User=oracle[Install]WantedBy=multi-user.target
Finally, indicate to the database to be brought up during boot.
# vim /etc/oratab
Find the mentioned line.
techoism:/u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1:N
Replace ?N? with ?Y?.
techoism:/u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1:Y
Reference: Know more about Oracle 12c Database
Enjoy it!
Originally published at https://www.techoism.com on April 15, 2019.