update : We have introduced an interactive learning platform to learn machine learning / AI , check out this blog in interactive mode.
Please visit the previous article to get comfortable with the math behind decision tree ID3 algo
Import the required libraries
import numpy as npimport pandas as pdeps = np.finfo(float).epsfrom numpy import log2 as log
?eps? here is the smallest representable number. At times we get log(0) or 0 in the denominator, to avoid that we are going to use this.
Define the dataset:
Create pandas dataframe :
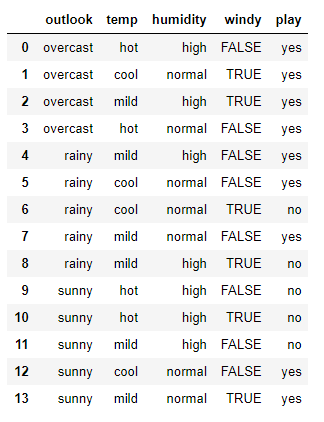
Now lets try to remember the steps to create a decision tree?.
1.compute the entropy for data-set2.for every attribute/feature: 1.calculate entropy for all categorical values 2.take average information entropy for the current attribute 3.calculate gain for the current attribute3. pick the highest gain attribute.4. Repeat until we get the tree we desired
- find the Entropy and then Information Gain for splitting the data set.
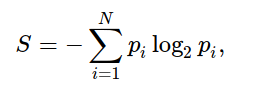
We?ll define a function that takes in class (target variable vector) and finds the entropy of that class.
Here the fraction is ?pi?, it is the proportion of a number of elements in that split group to the number of elements in the group before splitting(parent group).
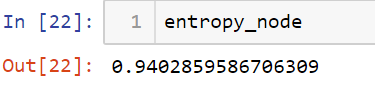 answer is same as we got in our previous article
answer is same as we got in our previous article
2 .Now define a function {ent} to calculate entropy of each attribute :
store entropy of each attribute with its name :
a_entropy = {k:ent(df,k) for k in df.keys()[:-1]}a_entropy
3. calculate Info gain of each attribute :
define a function to calculate IG (infogain) :
IG(attr) = entropy of dataset – entropy of attribute
def ig(e_dataset,e_attr): return(e_dataset-e_attr)
store IG of each attr in a dict :
#entropy_node = entropy of dataset#a_entropy[k] = entropy of k(th) attrIG = {k:ig(entropy_node,a_entropy[k]) for k in a_entropy}
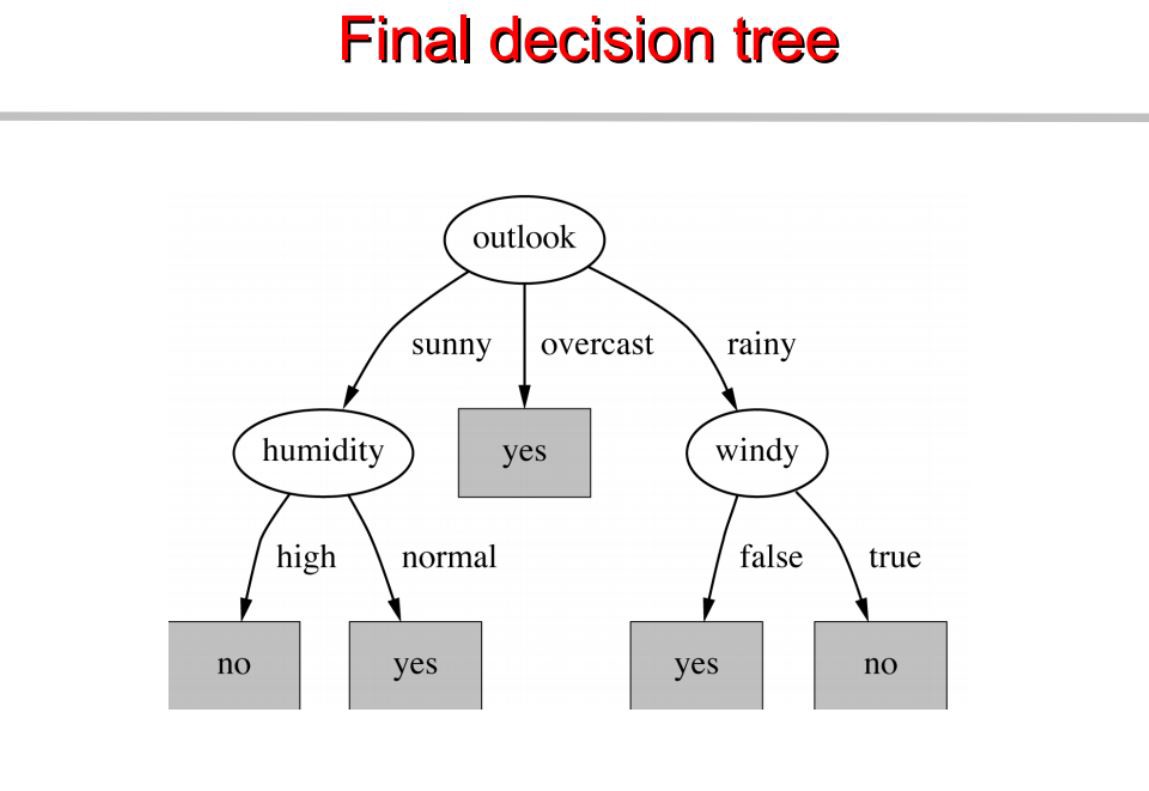
as we can see outlook has the highest info gain of 0.24 , therefore we will select outook as the node at this level for splitting.
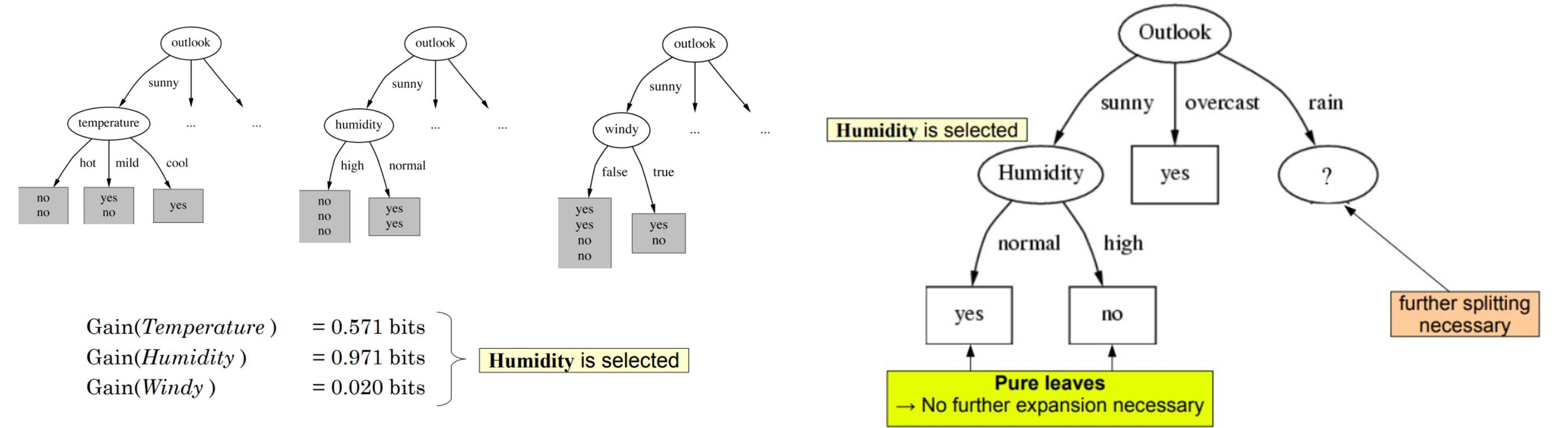
We build a decision tree based on this. Below is the complete code.
Code functions for building the tree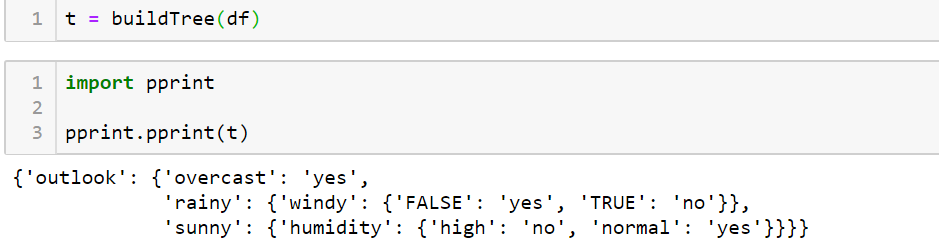
visit pytholabs.com for amazing courses

