Web browsers treat every element as a kind of box. However, CSS has two different types of boxes ? block and inline.
A block element always starts on a new line, and fills up the horizontal space left and right on the web page. You can add margins and padding on all four sides of any block element ? top, right, left, and bottom.
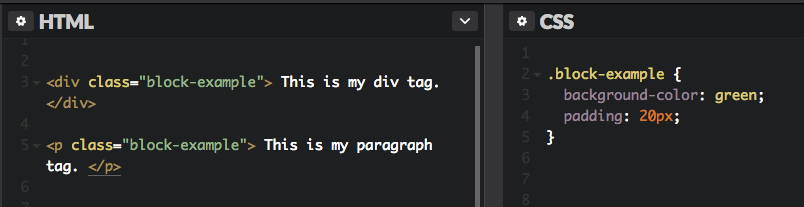
Some examples of block elements are <div> and <p> tags. As shown below, I?ve also added green padding on all four sides of each block element.

Inline Elements
Inline elements don?t start on a new line, they appear on the same line as the content and tags beside them. Some examples of inline elements are <span> , <strong>, and <img> tags.
When it comes to margins and padding, browsers treat inline elements differently. You can add space to the left and right on an inline element, but you cannot add height to the top or bottom padding or margin of an inline element.
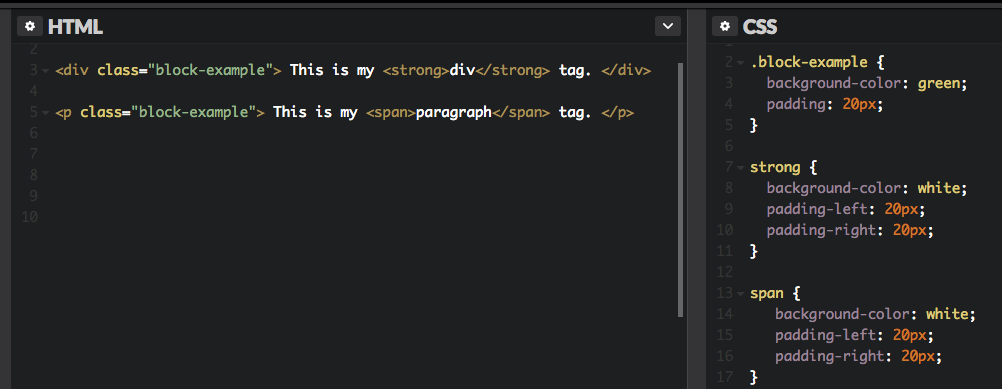
Inline elements can actually appear within block elements, as shown below. I?ve added white padding on the left and right side of each inline element.

Inline-Block
Inline-block elements are similar to inline elements, except they can have padding and margins added on all four sides. You?ll have to declare display: inline-block in your CSS code.
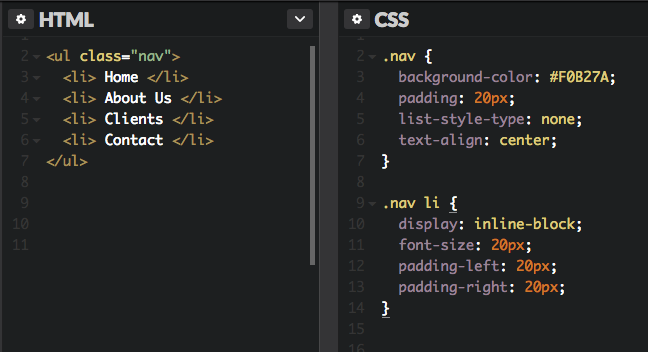
One common use for using inline-block is for creating navigation links horizontally, as shown below. I?ve created a horizontal navigation menu with an orange background color.

There are many other display properties out there as well, which you can check out via the MDN docs.
-D.

