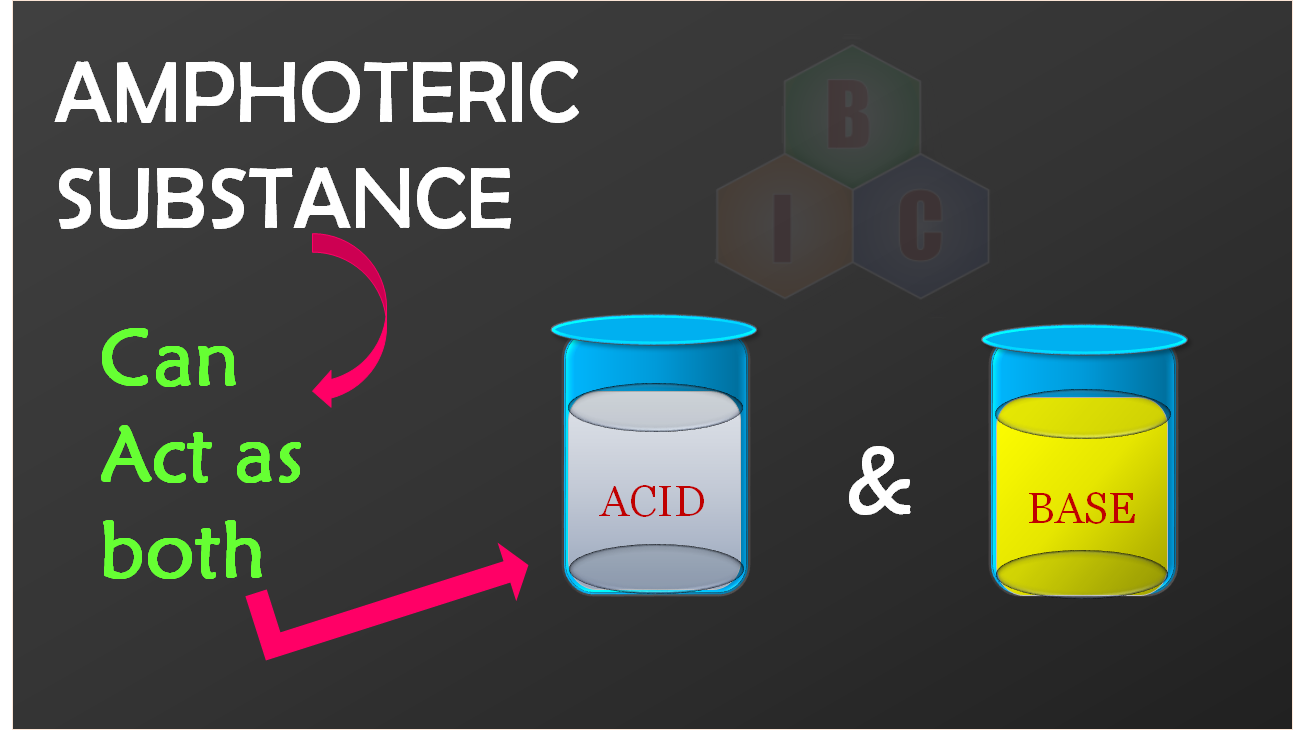
What are these Amphoteric compounds ?
Amphoteric compounds are chemical substance which might be a neutral molecule or an ionic molecule which can act both as an acid and a base in a chemical reaction. In fact the term Amphoteric is derived from the Greek word ?amphoteroi? meaning ?both?.
Note: Amphoteric substances are also called Amphiprotic substances.
The concept of Amphoteric compound can be well understood by Bronsted-Lowry concept of an acid and a base.
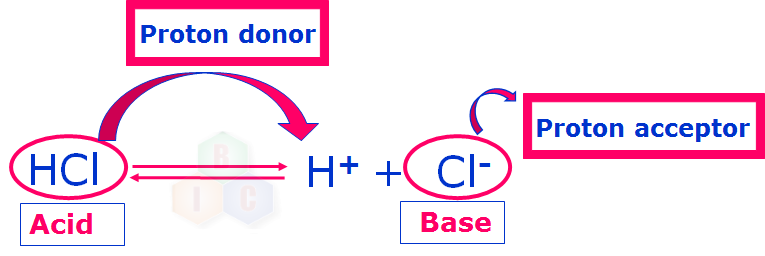
According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a substance which a can donate a proton while base is a substance which can accept a proton.

The Bronsted-Lowry concept of acid and base can be well understood by the following examples where a proton donor is called an acid while a proton acceptor is called a base.


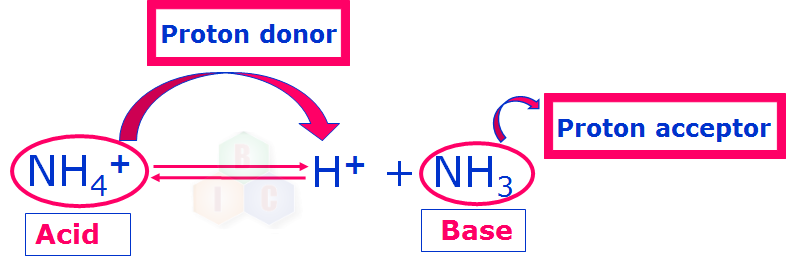
Now that we have understood about an acid and a base according to Bronsted-Lowry concept clearly, let us try to understand about this theory of Bronsted-Lowry in some more detail.
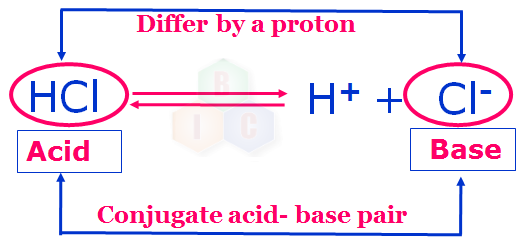
Bronsted-Lowry theory of acid and base includes in it the concept of conjugate acid-base pair. A pair of an acid and a base which differs by a proton is called a conjugate acid-base pair.
Now, let us try to understand clearly about conjugate acid-base pair. In example 1 shown above HCl and Cl- form a conjugate acid-base pair because they differ by a proton.
Similarly, NH4+ and NH3 in example 2 also form another conjugate acid-base pair.
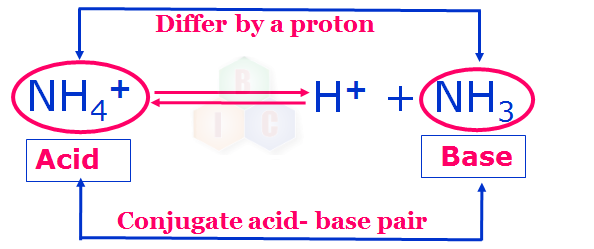
Note: If the Bronsted-Lowry acid is strong, its conjugate base pair will be weak and vice versa.
Now, how?s this conjugated acid-base pair going to help understand about Amphoteric substances?
To know the answer for this question let us look into the following reaction examples:
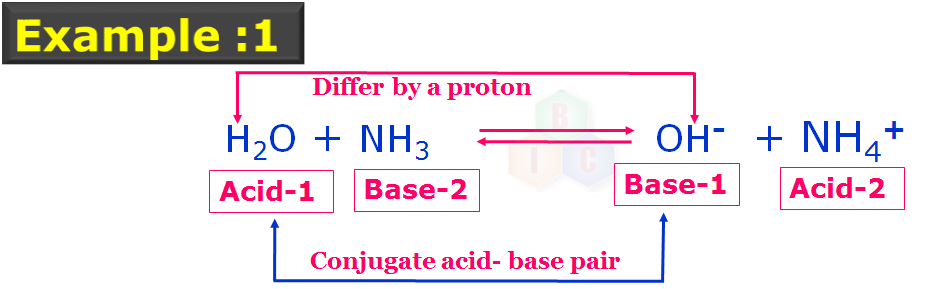
In this example 1: There are two pairs of conjugate acid-base pairs which are indicated with their nature and numbers. Acid-1 and Base-1 forms the one set conjugate acid-base pairs while Acid-2 and Base-2 forms another set of conjugate acid-base pairs as they also differ by a proton. In this example 1, note that, H2O is acting like an acid.
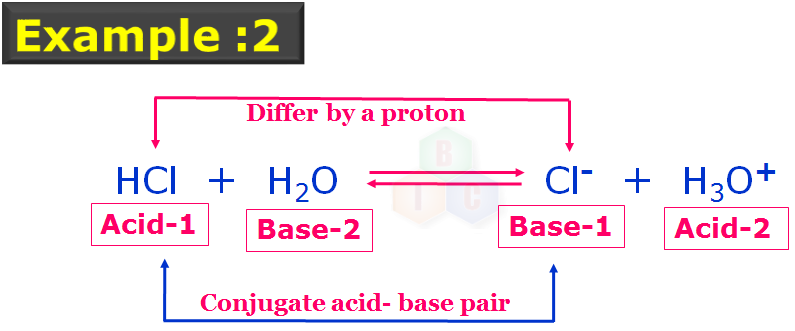
This example 2: also has two pairs of conjugate acid-base pairs which are indicated with their nature and numbers. Acid-1 and Base-1 forms the one set conjugate acid-base pairs while Acid-2 and Base-2 forms another set of conjugate acid-base pairs as they also differ by a proton. In this example 2 , note that, H2O is acting like a base.
In example 1, H2O is acting like an acid and in example 2, H2O is acting like a base, i.e., the same H2O molecule is acting as both an acid and a base in different reactions thus exhibiting its amphoteric nature.
Let us look into example 3 reaction equation:
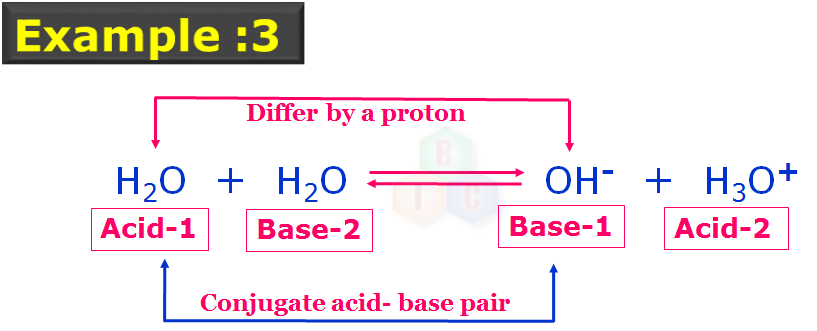
In this example 3: reaction we can see that H2O is acting like an acid and a base in the same reaction again illustrating its amphoteric nature.
Apart from H2O, ionic molecules like HCO3-, HSO4- also exhibit amphoteric nature.
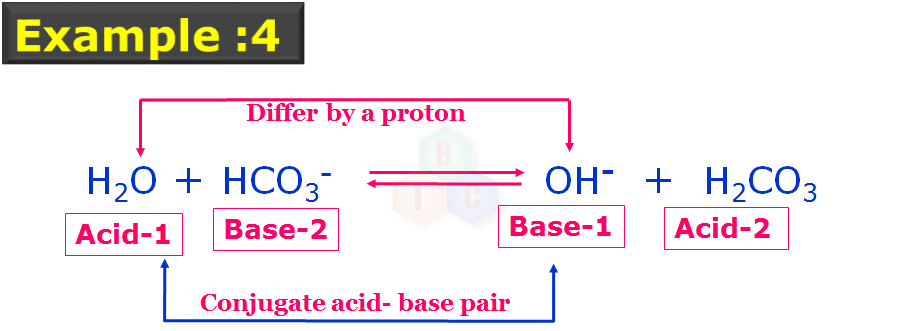
In this example 4: As you can see there two pairs of conjugate acid-base pairs which are indicated with their nature and numbers. Acid-1 and Base-1 forms the one set conjugate acid-base pairs while Acid-2 and Base-2 forms another set of conjugate acid-base pairs as they also differ by a proton. In this example 4, HCO3 – is acting like a base.
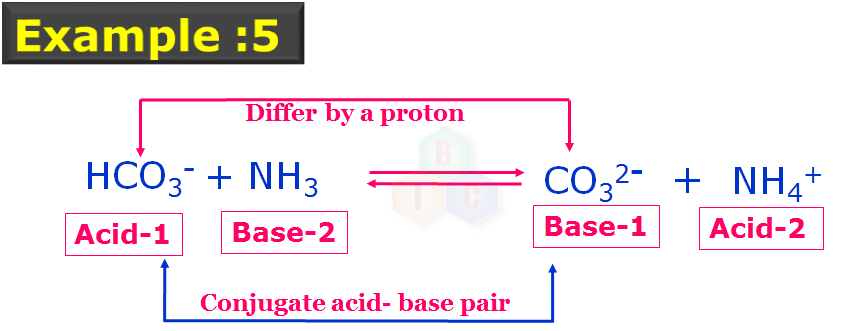
In this example 5: The two pairs of conjugate acid-base pairs which are indicated with their nature and numbers forming the corresponding set of conjugate acid-base pairs as they differ by a proton. In this example 5, HCO3- ? is acting like an acid.
Thus example reactions of 4 and 5 proves the amphoteric nature of bicarbonate ion (HCO3 -).
Work: Write the equations to show the amphoteric nature of HSO4- ion.
Do you Like this? Then Follow BIC at :
Follow BIC on Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/user/pucbic
Follow BIC on Facebook : http://facebook.com/bicspuc
Follow BIC on Instagram :https://www.instagram.com/bicpuc1/
Follow BIC on SoundCloud: https://soundcloud.com/bicpuc